Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) is essential for the success of organizations, particularly in regions undergoing rapid economic and social changes like the Middle East. SHRM aligns human resource practices with an organization’s strategic goals, ensuring the workforce drives long-term success.
In the Middle East, SHRM is vital due to the region’s cultural norms, economic diversification, and evolving labor markets. Ongoing economic reforms, especially in Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, emphasize the need for integrating HR strategies with broader business objectives.
In this blog we will explore Strategic Human Resource Management SHRM’s in the Middle East, focusing on its alignment with business goals, contribution to economic growth, and adaptation to cultural and organizational contexts.
Aligning HR Strategy with Business Goals
Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) ensures HR practices align with organizational and regional objectives. In the Middle East, companies must adapt their HR strategies to support national economic visions like Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030, which focuses on expanding non-oil industries and job creation. Aligning HR with these initiatives enhances both organizational success and regional development.
Additionally, companies must navigate cultural and regulatory challenges by complying with local labor laws and fostering people-centric policies like employee well-being. Engaging employees in strategic goals further ensures their roles contribute to the organization’s objectives, fostering a motivated and high-performing workforce.
The Role of Strategic HRM in Economic Growth
Here’s how SHRM contributes to growth:
Impact of Economic Reforms on HRM
Economic reforms across the Middle East, especially within the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) nations, have necessitated a shift in HR strategies to meet new economic demands. As these countries diversify beyond oil, sectors like technology, finance, and tourism have gained prominence.
SHRM plays a critical role by ensuring that HR policies and practices are adapted to support this transition, focusing on building a workforce that aligns with these emerging sectors.
This shift requires organizations to rethink traditional HR approaches, placing greater emphasis on developing skills that match the region’s evolving economic landscape and supporting sustainable growth initiatives.
Contribution to Organizational Performance and National Growth
SHRM not only improves individual organizational performance but also contributes to broader national economic growth. By aligning HR strategies with business objectives, companies can enhance efficiency, foster innovation, and respond effectively to market changes. The implementation of high-performance work practices (HPWPs) in the region has led to increased employee satisfaction and organizational citizenship behaviors, driving productivity and creating a more dynamic labor market.
Sectors Benefiting from SHRM in Middle East
Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) has significantly advanced key sectors across the Middle East, each leveraging SHRM to drive growth and maintain a competitive edge.
- In the public sector, SHRM has been vital in supporting government initiatives by developing talent management frameworks that attract and retain skilled professionals, aligning their capabilities with long-term national goals. This alignment has ensured the success of large-scale public projects requiring specialized expertise and a stable workforce.
- The healthcare sector, facing rapid growth and increasing demand for quality services, has benefited from SHRM by optimizing workforce planning, enhancing staff retention, and improving patient care outcomes. Similarly, the education sector has used SHRM to attract, develop, and retain the qualified educators necessary to deliver high-quality education in a changing academic landscape.
- In the private sector, industries such as finance and telecommunications have turned to SHRM to navigate a rapidly evolving market. By focusing on attracting and retaining top talent, these industries have secured the human capital needed to maintain their competitive position and drive innovation in an increasingly digital world.
Cultural and Organizational Norms in the Middle East
Cultural norms and organizational practices in the Middle East significantly influence the implementation of Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM). Understanding these factors is crucial for developing HR strategies that align with both local expectations and business objectives.
Influence of Cultural Norms on HR Practices
The region’s traditions, social expectations, and religious values create a unique environment that HR professionals must consider. Concepts like ‘wasta’—using connections in business dealings—are deeply ingrained, requiring HR strategies that respect these customs while promoting fairness and transparency.
Additionally, family ties and social networks often impact career advancement and job security. Effective HR strategies in the region must balance these cultural factors with a merit-based approach to talent management.
Comparison of SHRM Practices Between the Middle East and Western Countries
SHRM practices in the Middle East differ from those in Western countries due to cultural and organizational contexts. Western HR strategies often emphasize individual performance and autonomy, while Middle Eastern practices focus on collective well-being and social cohesion.
For example, performance appraisals in the Middle East may also consider an employee’s ability to maintain team harmony and align with cultural values, highlighting the need for culturally tailored HR approaches.
Case Studies: Multinational Corporations (MNCs) and Local Firms
MNCs and local firms in the Middle East often face challenges in aligning global HR practices with local cultural expectations. MNCs may need to adapt performance-based compensation and hierarchical structures to fit the region’s collectivist culture, while local firms must balance traditional practices with global standards.
Successful organizations are those that bridge the gap between global HR standards and local nuances.
Key Practices in Strategic Human Resource Management in Middle East
Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) involves key practices that align HR with organizational goals. In the Middle East, these practices are vital for adapting to economic changes and cultural contexts, ensuring organizational sustainability.
1. Talent Management and Development
In the Middle East, organizations place a strong emphasis on attracting, retaining, and developing talent to meet their business goals. SHRM focuses on creating comprehensive talent management strategies that include continuous learning, upskilling, and career development opportunities.
This helps organizations nurture a skilled workforce capable of meeting both current and future business needs. By investing in employee development, companies can reduce skill gaps and enhance overall productivity while fostering loyalty and engagement among their staff.
2. Workforce Localization Programs
Many Middle Eastern countries, especially Saudi Arabia and the UAE, have implemented workforce localization initiatives such as Saudization and Emiratization. These programs require organizations to hire and develop local talent to reduce dependency on expatriates.
SHRM focuses on aligning recruitment, training, and development strategies to support these goals. Companies must ensure compliance with these national policies while also building local workforce capabilities through tailored training programs and educational partnerships.
3. Cultural Sensitivity in HR Policies
With a highly diverse workforce in the Middle East, where multiple nationalities and cultures coexist, SHRM emphasizes cultural awareness and sensitivity. HR policies are designed to respect local customs, traditions, and religious practices, such as accommodating prayer times and observing local holidays.
At the same time, organizations need to foster inclusivity for expatriates by creating a culturally harmonious workplace. Strategic HR practices ensure that diversity management leads to better employee engagement and productivity.
4. Digital HR Transformation
The Middle East has seen rapid advancements in digital transformation, and HR functions are no exception. SHRM increasingly focuses on adopting cloud-based HR systems, AI-driven recruitment tools, and employee self-service platforms.
These technologies streamline HR operations, improve data-driven decision-making, and enhance employee experiences. By automating repetitive tasks like payroll and performance management, companies can focus on strategic initiatives that drive business growth and employee satisfaction.
5. Leadership Development and Succession Planning
Developing future leaders is a priority for organizations in the Middle East, particularly in family-owned businesses and government entities. SHRM practices include identifying high-potential employees and creating tailored leadership development programs to equip them with the necessary skills.
Succession planning ensures that there are capable leaders ready to step into key positions as the company grows or experiences transitions. This proactive approach reduces the risk of leadership gaps and ensures continuity in organizational strategy.
6. Employee Engagement and Well-being Programs
Organizations in the Middle East are increasingly recognizing the importance of employee engagement and well-being as part of their HR strategy. Initiatives such as flexible working arrangements, mental health support, wellness programs, and improved work-life balance policies are being implemented to retain top talent and reduce turnover.
SHRM practices focus on creating a positive work environment where employees feel valued, supported, and motivated, leading to higher productivity and loyalty.
7. Compliance with Labor Laws and Regulations
Each Middle Eastern country has its own set of labor laws and regulations, which are regularly updated to reflect changing economic and social conditions. SHRM ensures that HR policies and practices comply with local labor laws regarding employment contracts, wages, working hours, and employee benefits.
Strategic HR management involves staying updated with legal changes, ensuring fair treatment of employees, and minimizing legal risks. Non-compliance can result in penalties and damage to an organization’s reputation, so this aspect is a critical component of HR strategy.
Barriers and Challenges in Implementing Strategic HRM in Middle East
Implementing Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) in the Middle East comes with its own set of challenges. These challenges stem from deep-rooted cultural practices, complex regulatory environments, and organizational resistance to change. Here are some of the key barriers:
Resistance to Change
Many organizations in the Middle East still follow traditional HR practices, focusing more on administration than strategy. Introducing SHRM often meets resistance, as employees and management may fear the changes it brings, such as job restructuring or increased responsibilities.
This hesitation makes it difficult to shift to a more strategic HR approach, slowing down its adoption and effectiveness.
To overcome resistance, companies should focus on change management strategies that include clear communication, employee involvement, and gradual implementation. Engaging employees early in the process, explaining the benefits of SHRM, and addressing their concerns can help reduce resistance. Leadership should act as role models in embracing change to set the tone for the rest of the organization.
Lack of HR Analytics and Data-Driven Decision Making
Many organizations in the Middle East are yet to fully adopt HR analytics. Without data-driven insights, it becomes difficult to measure the effectiveness of HR strategies or make informed decisions.
Organizations should invest in HR analytics tools and training to enhance their ability to collect, analyze, and interpret workforce data. By using data to identify trends, predict employee behaviors, and measure success, HR can become a strategic partner in driving business goals.
Gender Inequality in the Workforce
While there has been progress in recent years, gender inequality remains an issue in certain parts of the Middle East. This disparity limits the talent pool, especially when companies aim to diversify leadership roles or implement inclusive HR policies.
Companies can address gender inequality by promoting equal opportunities in recruitment, development, and leadership roles. Implementing policies that support work-life balance, such as flexible work arrangements and parental leave, can help encourage more women to join and remain in the workforce.
Additionally, diversity and inclusion programs can foster a culture that values and supports gender equality. Mentorship and leadership development programs specifically designed for women can help bridge the gap and promote greater female representation in higher-level roles.
Policy and Regulatory Constraints
The complex regulatory environment also poses challenges for SHRM. Varying labor laws and nationalization policies, such as Emiratization and Saudization, can restrict HR flexibility.
Organizations must navigate these constraints while aligning HR strategies with business goals, often requiring creative solutions like specialized training programs.
Overcoming these challenges requires building strong relationships with stakeholders and leveraging technology to streamline HR processes. For example, HR analytics can help organizations meet regulatory requirements and identify areas for talent development, ensuring both compliance and strategic success.
Future Directions and Recommendations for Middle East SHRM
Enhancing SHRM Practices for Better Alignment
As the Middle East undergoes a significant economic transformation, the role of Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) is becoming more critical than ever.
Organizations must go beyond traditional HR practices to implement more sophisticated and adaptable approaches that align directly with their long-term business objectives. This alignment is not just about meeting immediate workforce needs but ensuring that HR strategies are embedded in the overall vision for sustainable growth.
Key areas such as recruitment, training, and performance management need to be constantly updated to reflect both the organization’s evolving priorities and the unique demands of the regional economy.
By adopting SHRM practices that prioritize flexibility and adaptability, companies can foster a culture of continuous improvement. This approach allows organizations to stay agile and proactive in responding to shifting market conditions, ensuring they maintain a competitive edge in a rapidly changing environment.
The Role of Technology and Innovation in SHRM
Technology is set to transform the landscape of Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) in the Middle East. Advanced analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and digital platforms offer HR professionals new tools to make data-driven decisions, streamline operations, and enhance employee engagement. These technologies can simplify routine tasks, reduce administrative burdens, and provide real-time insights into workforce trends.
For example, AI-driven tools can identify potential skill gaps, forecast employee turnover, and even suggest personalized learning and development programs. Additionally, automation can improve recruitment by screening candidates efficiently and providing tailored onboarding experiences. By adopting these innovations, organizations can elevate their HR strategies to align closely with long-term business goals, fostering both agility and resilience in the rapidly evolving corporate world.
Embracing technology not only helps organizations operate more efficiently but also positions them as forward-thinking employers, capable of attracting and retaining top talent in an increasingly competitive environment.
Recommendations for Policymakers and HR Practitioners
Policymakers in the Middle East should continue to support initiatives that promote the development of a skilled and competitive workforce. This includes creating more flexible labor regulations that encourage innovation while still protecting workers’ rights.
Additionally, HR practitioners should focus on developing culturally sensitive strategies that bridge the gap between traditional practices and modern HR approaches. By doing so, they can create more inclusive and effective HR systems that contribute to both organizational and national growth.
Conclusion
Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) is crucial for driving organizational success and contributing to economic growth in the Middle East. By aligning HR practices with business goals and embracing technology, companies can overcome cultural and regulatory challenges to create a future-ready workforce.
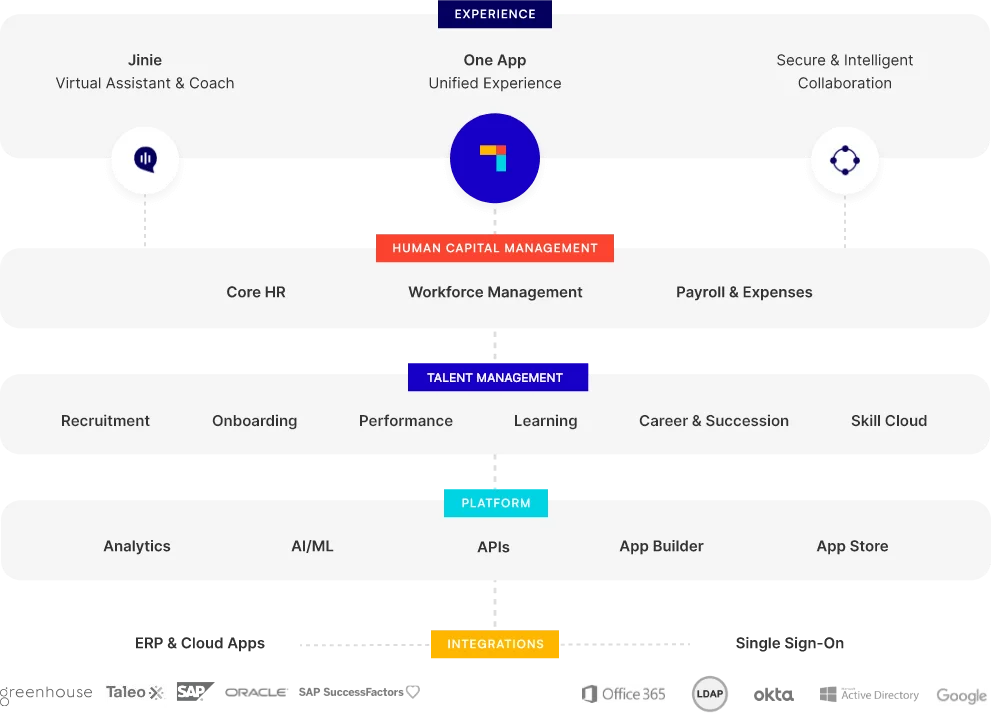
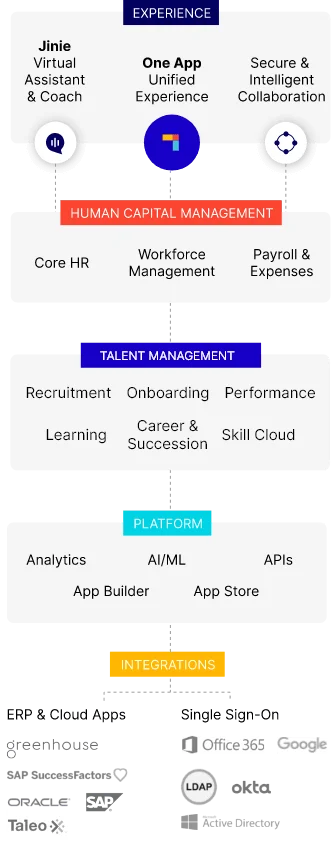
For organizations aiming to enhance their SHRM practices, platforms like PeopleStrong provide a comprehensive solution. As a leading HCM platform in APAC, PeopleStrong integrates AI-driven insights, scalable architecture, and mobile-first experiences to simplify HR processes across the employee life cycle. By leveraging PeopleStrong’s SaaS platform, companies can streamline recruitment, manage talent effectively, and ensure their workforce is equipped to meet future challenges.
To ensure your organization remains at the forefront of HR innovation, consider adopting PeopleStrong’s HR tech suite. Empower your HR team to build a connected, agile, and future-ready workforce that drives sustained growth.