Human Resource Development (HRD) has become increasingly vital in the Middle East as the region strives to meet ambitious goals like Saudi Vision 2030. HRD is essential for cultivating a skilled workforce that can support economic diversification and sustainable growth.
According to a World Economic Forum report, the Middle East will need to reskill more than 50% of its workforce by 2025 to keep pace with technological changes and industry demands.
The digital economy in the Middle East is expected to contribute $230 billion by 2023, highlighting the urgent need for HRD initiatives that equip workers with the necessary skills.
By aligning HRD strategies with national goals, countries in the region aim to reduce their reliance on oil—currently accounting for around 30% of the GDP in some economies—and build a more diversified and resilient economic base.
Moreover, HRD plays a crucial role in enhancing employee satisfaction and retention. Companies that invest in comprehensive training programs can reduce turnover rates by up to 24%, fostering a more committed and productive workforce.
Thus, HRD is not just a tool for immediate skill development but a strategic approach to ensuring long-term economic and organizational success.
Types of Human Resource Development Programs
Human Resource Development (HRD) programs in the Middle East are diverse, reflecting the region’s commitment to building a skilled and adaptable workforce. These programs are designed to meet the specific needs of different industries while aligning with broader national development goals.

1. Training and Development Programs
Training and development programs are the foundation of HRD, focusing on equipping employees with the skills needed for their current roles and future growth.
In the Middle East, initiatives like the UAE’s National Program for Advanced Skills demonstrate the region’s emphasis on preparing a workforce capable of adapting to both technical and soft skill demands. These programs are critical in meeting the needs of rapidly evolving industries.
2. Leadership Development Programs
Leadership development is essential for cultivating the next generation of leaders. These programs focus on building strategic thinking, decision-making, and management skills.
In the context of nationalization efforts such as Emiratization and Saudization, these programs ensure that local talent is well-prepared to take on leadership roles that were traditionally occupied by expatriates.
3. Performance Management Systems
Performance management systems are integral to aligning individual employee goals with the broader objectives of the organization. These systems provide a structured approach to regularly assess and improve performance, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Companies in Saudi Arabia, for instance, are adopting advanced performance management tools to enhance productivity and engagement.
4. Talent Management and Succession Planning
Talent management and succession planning are strategic HRD practices focused on identifying and nurturing high-potential employees. These programs ensure that organizations have a pipeline of skilled individuals ready to step into key roles.
With initiatives like Qatar’s National Vision 2030, succession planning is becoming increasingly important to maintain leadership continuity in the region.
5. Educational and Professional Development
Educational and professional development opportunities, such as certifications, workshops, and continuing education, are widely promoted across the Middle East.
Collaborative efforts between corporations and educational institutions are growing, providing employees with access to advanced learning that supports both personal and organizational development.
Objectives of Human Resource Development in the Middle East
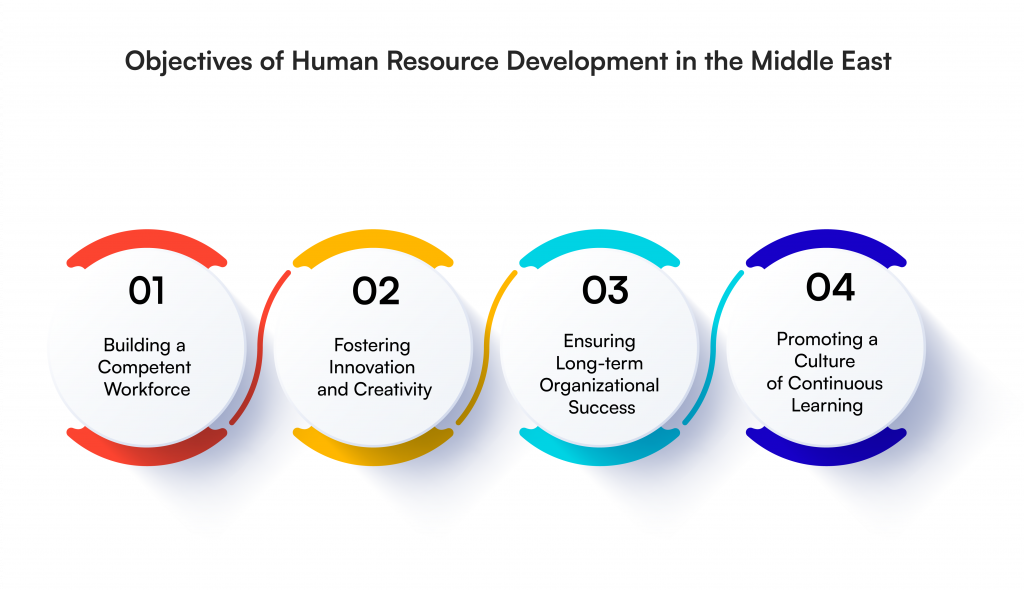
1. Building a Competent Workforce
One of the primary objectives of HRD in the Middle East is to establish a workforce that is well-equipped to meet the region’s economic and industry-specific demands.
As countries diversify their economies beyond oil, there is an increasing need for skilled professionals in sectors such as technology, healthcare, and renewable energy. HRD initiatives are essential in developing these competencies to ensure economic resilience and growth.
2. Fostering Innovation and Creativity
HRD plays a crucial role in promoting a culture of innovation and creativity. By encouraging continuous learning and providing opportunities for skill enhancement, HRD helps employees think outside the box and contribute new ideas.
This focus on innovation is particularly important as Middle Eastern countries seek to position themselves as leaders in areas like smart technology, sustainable development, and entrepreneurship.
3. Ensuring Long-term Organizational Success
Aligning HRD initiatives with organizational goals is key to ensuring long-term success. By developing employees who are not only skilled but also aligned with the strategic objectives of their organizations, HRD contributes to sustainable growth. This alignment is vital for companies in the Middle East that are navigating rapid economic changes and aiming to maintain their competitive edge.
4. Promoting a Culture of Continuous Learning
Creating an environment that encourages ongoing skill enhancement and professional growth is another important objective of HRD.
In the Middle East, where industries are evolving quickly, fostering a culture of continuous learning helps employees stay relevant and adaptable. This focus on lifelong learning is essential for both individual career development and the overall progress of the region’s workforce.
Challenges and Considerations in Human Resource Development Implementation in Middle Eastern Companies
1. Cultural Sensitivity
Cultural sensitivity is a critical challenge in implementing Human Resource Development (HRD) across the Middle East. The region is characterized by a rich tapestry of cultures, each with its unique customs, values, and social norms. This diversity necessitates HRD strategies that are not only effective but also deeply respectful of local traditions.
For example, while introducing new training methods or leadership styles, HR professionals must ensure these initiatives are culturally appropriate and do not conflict with deeply rooted societal expectations. Successfully navigating this complexity requires a nuanced understanding of the cultural landscape, fostering a work environment where modern HR practices can coexist with traditional values.
2. Balancing Traditional and Modern Approaches
The Middle East presents a unique challenge in balancing the preservation of traditional values with the integration of modern HR practices. In many organizations, there is a strong emphasis on maintaining cultural heritage, which can sometimes be at odds with the adoption of contemporary HR methods such as digital training platforms or data-driven performance evaluations.
Companies must carefully navigate this balance, ensuring that new practices enhance rather than diminish traditional values. This delicate equilibrium is crucial for gaining employee buy-in and ensuring that HRD initiatives are both effective and culturally resonant. The challenge lies in innovating without alienating the workforce or undermining the values that have historically shaped the business environment.
3. Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations are pivotal in shaping HRD strategies in the Middle East. Nationalization initiatives like Saudization in Saudi Arabia and Emiratization in the UAE require companies to prioritize the development and employment of local talent. These policies aim to reduce dependency on expatriate labor and foster economic diversification, but they also pose significant challenges.
Companies must align their HRD initiatives with these regulatory requirements, which may involve overhauling existing recruitment and training processes. The implementation of such policies often requires substantial investment in training and development programs tailored to the local workforce, ensuring compliance while also striving to meet business objectives.
Moreover, the regulatory landscape is continuously evolving, necessitating ongoing adjustments to HR strategies to stay compliant and competitive.
4. Economic Fluctuations and Market Dynamics
The Middle Eastern economy is subject to significant fluctuations due to its heavy reliance on oil and gas revenues. These economic dynamics can directly impact HRD initiatives, as companies may need to adjust their strategies in response to market conditions.
For instance, during periods of economic downturn, organizations might face budget constraints that limit their ability to invest in training and development programs. Conversely, during economic booms, there may be a heightened focus on rapidly upskilling the workforce to meet increased demand.
HR professionals must be adept at navigating these economic shifts, ensuring that HRD initiatives remain aligned with the company’s strategic goals while also being flexible enough to adapt to changing economic realities.
5. Technological Advancements
As the Middle East continues to embrace digital transformation, the integration of technology into HRD poses both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, advanced technologies such as AI-driven learning platforms and virtual training environments offer innovative ways to enhance employee development.
However, the rapid pace of technological change can also create a skills gap, where the existing workforce may struggle to keep up with new tools and platforms. Companies must therefore invest not only in cutting-edge HR technologies but also in the continuous upskilling of their employees to fully leverage these advancements. The challenge lies in ensuring that technology serves as an enabler of HRD rather than a source of disruption.
Conclusion
Human Resource Development (HRD) is essential for the Middle East’s future, addressing both current economic needs and long-term goals. By building a skilled workforce, promoting innovation, and fostering continuous learning, HRD drives economic growth and sustainability.
While challenges exist, such as balancing cultural traditions with modern practices and aligning with government policies, strategic HRD initiatives can overcome these hurdles. As the Middle East pursues ambitious national visions, HRD will play a crucial role in shaping a resilient and diverse economy.
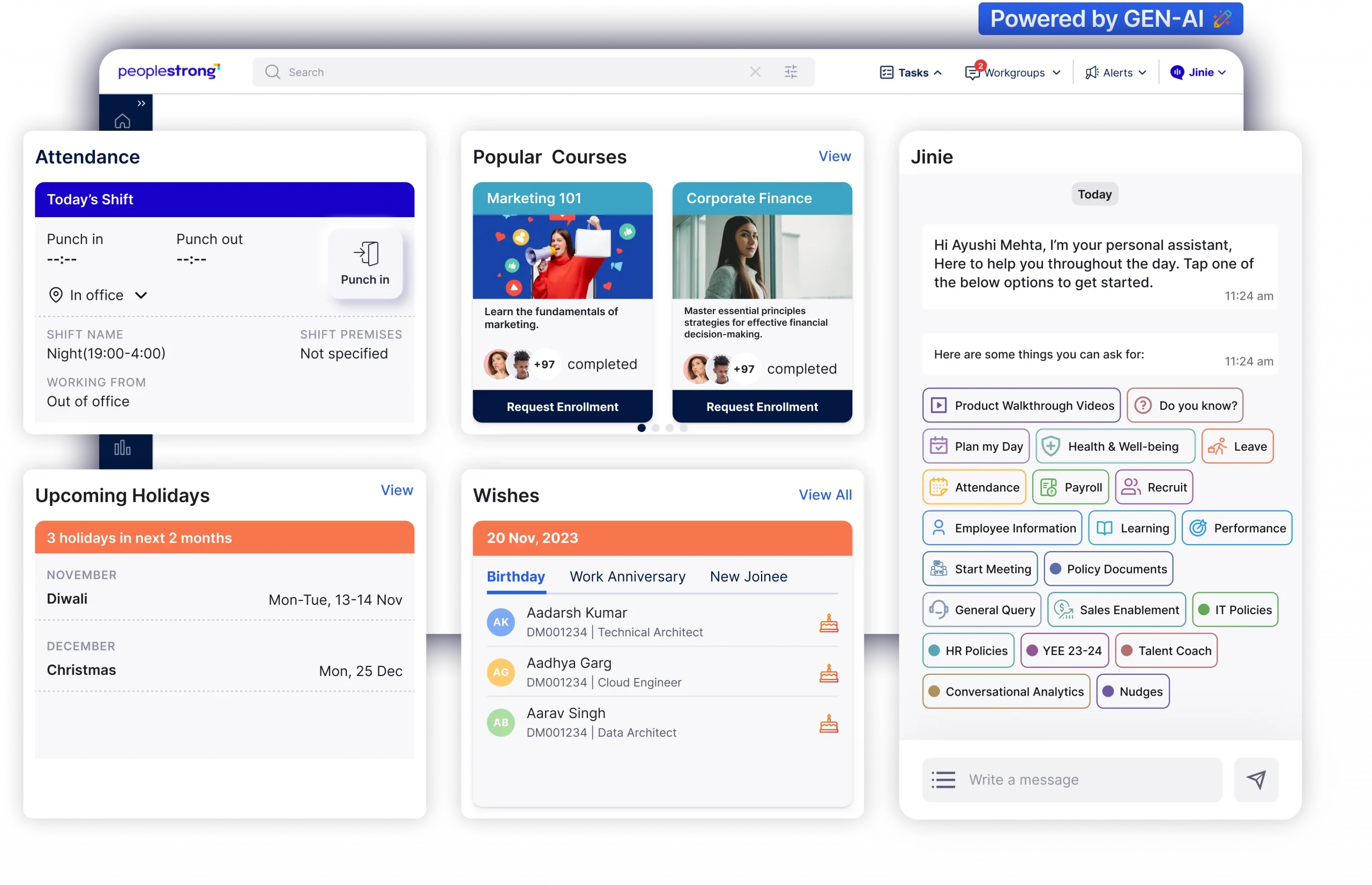
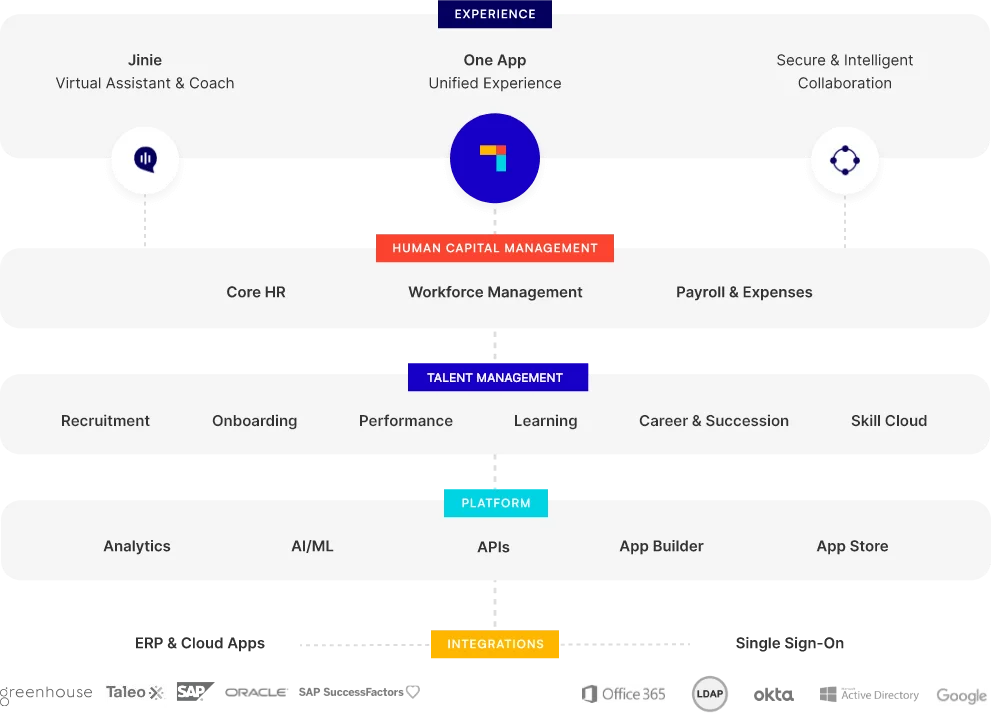
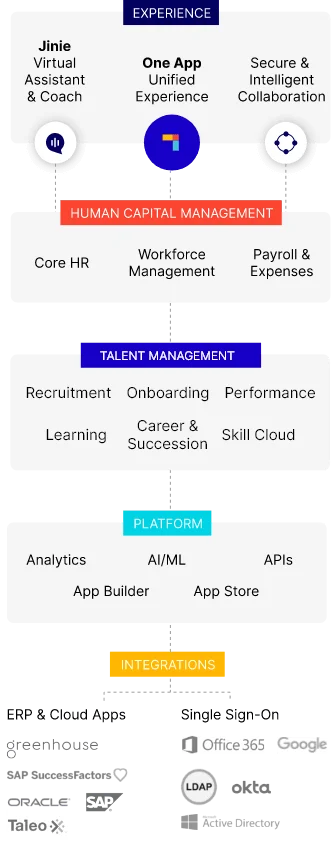
Platforms like PeopleStrong are vital in this effort. PeopleStrong offers a unified HR solution that breaks data silos, providing a single source of truth for all HR data. With features like instant access to workforce data, dynamic organization charts, and seamless integration with payroll, PeopleStrong helps businesses manage HR processes efficiently and securely.
Elevate your HR strategy with PeopleStrong’s integrated solutions. Build a future-ready workforce and lead your organization toward success. Discover how PeopleStrong can transform your HR today.