HR policies are at the heart of managing employees effectively, and they play a vital role in driving an organization’s success. In the Middle East, where businesses face unique challenges, having clear and well-thought-out HR policies is essential.
These policies help companies navigate everything from hiring and compensation to how employees are treated daily. They also ensure that organizations meet legal requirements and foster a positive workplace culture.
In this blog, I’ll walk you through the key HR policies that every organization in the region should have.
Understanding HR Policies
HR policies are the guidelines that shape how an organization manages its workforce. These policies cover everything from hiring practices and employee benefits to performance management and workplace conduct. Essentially, they are the rules that ensure fairness, consistency, and legal compliance in how employees are treated.
Having well-defined HR policies is crucial for any organization. They provide a clear framework that helps prevent misunderstandings and disputes between employees and management. When everyone knows the rules and expectations, it creates a smoother, more efficient working environment.
Moreover, these policies protect both the company and its employees by ensuring that all practices are in line with local laws and regulations. This not only helps in maintaining a positive work atmosphere but also safeguards the organization from potential legal issues.
Legal Framework
Understanding the legal framework that governs HR policies is essential for any organization operating in the Middle East. Each country in the region has its own set of labor laws that dictate how employers and employees should interact. These laws cover a wide range of issues, including employment contracts, working hours, leave entitlements, and termination procedures.
While there are similarities across the region, key differences exist between countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE.
For instance, in Saudi Arabia, written employment contracts are mandatory and usually span two years, with specific regulations on probation periods and termination. In contrast, the UAE has a more flexible approach, allowing for various types of employment contracts, including fixed-term, part-time, and temporary agreements.
These differences highlight the importance of tailoring HR policies to meet the specific legal requirements of each country. Failing to comply with local laws can lead to severe penalties, including fines, legal disputes, and even the loss of business licences.
Therefore, it is crucial for organizations to stay informed about the legal landscape and regularly review their HR policies to ensure they remain compliant.
Must-Have HR Policies for Middle Eastern Organizations
Establishing effective HR policies is crucial for businesses in the Middle East. These policies should address local labor laws, cultural considerations, and best practices in employee management. Here are the HR policies for companies in the Middle East.
1 Employment Contract Policies
One of the foundational elements of any HR policy is the employment contract. In the Middle East, a written contract is not just a formality—it’s a legal requirement. These contracts provide clarity on the relationship between the employer and the employee, outlining everything from job responsibilities to compensation.
1.1 Employment Contract
A written employment contract ensures that both parties are clear about their rights and obligations. It serves as a binding agreement that details the terms of employment, including job title, salary, benefits, and work conditions. This document is crucial in protecting both the employer and the employee by setting clear expectations and reducing the risk of misunderstandings.
An employment contract in this region typically includes several key elements. These include the names and addresses of the employer and employee, the job description, the duration of the contract, compensation details, benefits, and provisions for dispute resolution. Each of these components is vital to ensuring that the employment relationship is clear and legally sound.
1.2 Probation Period
- Standard Duration: The probation period is a common practice in many organizations, allowing both the employer and employee to assess their fit for the role. In the Middle East, the standard probation period usually lasts up to 90 days, though it can be extended to 180 days by mutual agreement. During this time, both parties have the opportunity to evaluate the working relationship without the full commitment of a long-term contract.
- Termination During Probation: If the employment is terminated during the probation period, specific rules apply. Either party can end the employment without the standard notice period, but it’s essential to ensure that all terms regarding termination during this period are clearly outlined in the contract. This protects both parties and ensures that the termination process is fair and transparent.
2 Working Hours and Leave Policies
2.1 Working Hours and Overtime
- Standard Working Hours: Working hours are a critical aspect of HR policies, particularly in the Middle East where labor laws strictly regulate the workweek. Typically, employees are expected to work 8 hours a day, 48 hours a week. However, during the holy month of Ramadan, Muslim employees often have reduced working hours, which is a significant consideration for businesses operating in the region.
- Overtime Compensation: Overtime work is common, but it comes with specific legal requirements. Employees are entitled to extra pay for any hours worked beyond the standard workweek. The rate for overtime is usually set at 150% of the regular hourly wage, and there are limits on how much overtime can be worked in a single day or week. It’s essential for HR policies to clearly define how overtime is calculated and compensated to ensure compliance with local laws and to avoid disputes.
2.2 Leave Policies
- Annual Leave: Employees are entitled to a certain number of days off each year as part of their annual leave. In the Middle East, this entitlement typically increases with the length of service. For instance, employees may start with 21 days of paid annual leave per year, which can increase over time. HR policies should clearly outline the leave accrual process, how leave requests are handled, and any restrictions on when leave can be taken.
- Sick Leave: Sick leave is another important aspect of HR policies. Employees are entitled to take time off if they are unwell, and they should receive a portion of their regular pay during this period. The exact terms of sick leave, including the duration and pay, can vary depending on the country and specific company policies. It’s crucial to have clear guidelines in place so employees know their rights and responsibilities if they need to take sick leave.
- Maternity and Paternity Leave: Parental leave is increasingly recognized as essential for supporting employees with families. In the Middle East, maternity leave is typically provided for a period ranging from 45 to 90 days, depending on the country and the length of service. Paternity leave is less common but is starting to gain traction in some countries. These policies should be clearly defined to support employees during significant life events while ensuring compliance with local labor laws.
2.3 Public Holidays
Public holidays vary across the Middle East, with each country having its own set of national and religious holidays. Common holidays include Eid al-Fitr, Eid al-Adha, and National Day.
Employees are typically entitled to take these days off with full pay. If employees are required to work on a public holiday, they should be compensated at a higher rate or given a day off in lieu. HR policies must specify the treatment of public holidays, including any special arrangements for those who work on these days.
3 Compensation and Benefits Policies
3.1 Compensation Policy
- Salary Administration: Managing salaries is a fundamental part of HR policies. It’s essential for companies to have a structured approach to setting and reviewing salaries. This process should consider factors such as the employee’s role, experience, and the industry standard. Regular reviews ensure that salaries remain competitive, helping to attract and retain top talent. HR policies should clearly outline how salaries are determined, when reviews will take place, and how any adjustments will be communicated to employees.
- End-of-Service Benefits: In many Middle Eastern countries, end-of-service benefits are a legal requirement. These benefits provide a financial cushion for employees who leave the company after a certain period of service. The calculation usually depends on the length of service and the employee’s last drawn salary. For example, an employee might be entitled to a certain number of days’ pay for each year of service, with the amount increasing after a specific threshold. It’s crucial to detail these benefits in the HR policy to ensure transparency and compliance with local laws.
3.2 Allowances
Many companies in the region offer additional allowances to cover costs such as housing and transportation. These allowances are often a significant part of the overall compensation package, especially in countries where the cost of living is high.
HR policies should specify who is eligible for these allowances, how the amounts are determined, and the process for disbursing them. Clear guidelines help employees understand their entitlements and prevent any potential disputes.
3.3 Health Insurance
Providing health insurance is not just a benefit; in many cases, it’s a legal obligation. Employers are required to offer health insurance that covers basic medical needs. This insurance should extend to the employee and, in some cases, their dependents.
HR policies need to clearly define the scope of coverage, the process for accessing health services, and the responsibilities of both the employer and the employee. This ensures that employees feel secure knowing that their health needs will be taken care of.
4 Recruitment and Hiring Policies
4.1 Recruitment Procedures
- Job Advertising and Application Processing: Recruitment starts with job advertising, and in the Middle East, there are specific legal requirements that companies must follow when posting job openings. For example, in the UAE, job postings may need to be listed on government portals like the Ministry of Human Resources and Emiratization (MOHRE) website. HR policies should outline the steps for advertising job vacancies, including the platforms to be used and the timeline for application processing. This helps ensure that the recruitment process is transparent, fair, and compliant with local regulations.
- Selection Process: The selection process is a critical step in hiring the right candidate. It involves screening applications, conducting interviews, and making final decisions. HR policies should provide a clear framework for these steps, detailing who is involved in the selection process, how candidates are evaluated, and the criteria for making hiring decisions. This structure helps in maintaining consistency and fairness throughout the recruitment process, ensuring that all candidates are assessed on an equal basis.
4.2 Non-Discrimination Policy
- Equal Opportunity: Non-discrimination is a key principle that should be embedded in every stage of the recruitment process. HR policies must clearly state that hiring decisions will be made based on merit, without bias related to gender, race, religion, nationality, or any other protected characteristic. This commitment to equal opportunity not only fosters a diverse and inclusive workplace but also helps the company comply with anti-discrimination laws that are increasingly enforced across the region. Clear guidelines should be provided on how to handle complaints or concerns about discrimination to ensure a safe and fair working environment for all employees.
5 Performance Management and Employee Development
5.1 Performance Management
- Appraisal Systems: Effective performance management is essential for maintaining high standards and fostering employee growth. HR policies should include a well-defined appraisal system that outlines how employee performance will be evaluated. This system typically involves setting clear objectives at the beginning of the performance period and conducting regular reviews to assess progress. The appraisal process should be transparent, with employees receiving constructive feedback that helps them improve and align their efforts with the organization’s goals. Regular appraisals also provide an opportunity to identify high performers who may be eligible for promotions or other rewards.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Continuous feedback is crucial for employee development. HR policies should encourage managers to provide regular, real-time feedback rather than waiting for annual reviews. This can be done through informal check-ins, structured meetings, or using performance management tools that track progress throughout the year. Effective feedback helps employees understand their strengths and areas for improvement, fostering a culture of continuous learning and development.
5.2 Training and Development
Investing in employee training and development is key to building a skilled and motivated workforce. HR policies should outline the opportunities available for professional growth, including training programs, workshops, and access to further education.
Companies may also consider offering mentoring programs or leadership development courses to help employees advance in their careers. Clear guidelines on how employees can apply for or be selected for these opportunities ensure that all staff members have the chance to develop their skills and contribute more effectively to the organization.
6 Workplace Conduct and Safety
6.1 Anti-Harassment Policy
- Defining Harassment: In the Middle East, creating a safe and respectful workplace is a legal and cultural necessity. Harassment, including sexual harassment, bullying, and any form of discrimination, is strictly prohibited. For instance, in the UAE, anti-harassment policies must be clear in defining what constitutes unacceptable behavior. This includes any conduct that creates an intimidating, hostile, or offensive work environment. The policy should also reflect the cultural sensitivities of the region, ensuring that all employees, regardless of nationality or gender, feel safe and respected.
- Reporting and Investigation: Middle Eastern countries such as Saudi Arabia and the UAE have specific guidelines on handling harassment claims. HR policies must provide a clear process for reporting harassment, which should include confidential channels like designated HR personnel or anonymous hotlines. The investigation process needs to be thorough and impartial, with a strong emphasis on protecting the confidentiality of all parties involved. In the UAE, for example, companies are required to handle such complaints seriously and ensure that investigations are conducted in a manner that is both fair and discreet.
6.2 Workplace Safety
- Health and Safety Measures: In the Middle East, workplace safety is governed by strict regulations. For instance, the UAE’s Labor Law mandates that employers provide a safe working environment that prevents health hazards and accidents. HR policies must include comprehensive health and safety guidelines that comply with local laws. This includes regular safety audits, employee training on health and safety procedures, and the provision of necessary safety equipment. Saudi Arabia also places a strong emphasis on safety, particularly in industries like construction and manufacturing, where strict adherence to safety protocols is required.
- Emergency Procedures: Emergency preparedness is a critical component of workplace safety in the Middle East. HR policies should detail specific emergency procedures, including evacuation plans, emergency contact numbers, and the roles of specific individuals during an emergency. In countries like the UAE, companies are required to conduct regular drills and ensure that all employees are familiar with these procedures. This preparation is vital for minimizing risks during emergencies, such as fires or natural disasters.
6.3 Code of Conduct
The Code of Conduct in Middle Eastern workplaces must reflect both the organizational values and the cultural norms of the region. In the UAE and Saudi Arabia, HR policies should emphasize professionalism, ethical behavior, and respect for cultural and religious practices.
This includes guidelines on appropriate dress codes, respectful interactions with colleagues, and adherence to local customs and traditions. The Code of Conduct should be clearly communicated to all employees, ensuring they understand the expectations and the consequences of non-compliance.
7 Termination and Exit Policies
7.1 Termination Procedures
- Grounds for Termination: In the Middle East, termination procedures are strictly regulated, with clear guidelines set out in labor laws. For example, in Saudi Arabia, an employment contract can be terminated for reasons such as mutual consent, the completion of the contract period, or retirement. However, it’s important for HR policies to detail the specific grounds under which termination can occur, including poor performance, misconduct, or redundancy. In the UAE, termination without notice is permissible in cases of gross misconduct, but this must be well-documented and justified to avoid legal repercussions.
- Notice Periods: Notice periods in the Middle East vary depending on the country and the nature of the employment contract. In Saudi Arabia, the standard notice period is 60 days for an indefinite-term contract, while in the UAE, the notice period is typically 30 days. HR policies should clearly outline the required notice periods for both the employer and the employee, ensuring that all parties are aware of their obligations during the termination process. It’s also important to consider any specific provisions in the contract that might override the standard notice periods.
7.2 End of Service Benefits
End-of-service benefits (EOSB) are a critical component of termination policies in the Middle East. In both Saudi Arabia and the UAE, employees are entitled to a gratuity payment at the end of their service, calculated based on their length of service and final salary.
For example, in the UAE, employees who have completed at least one year of continuous service are entitled to 21 days’ wage for each of the first five years of service and 30 days’ wage for each additional year. HR policies must clearly explain how these benefits are calculated, including any deductions that might apply, to ensure transparency and compliance with local laws.
7.3 Exit Interviews
Exit interviews are an important part of the termination process, providing valuable insights into the employee experience and helping organizations improve retention strategies. In the Middle East, exit interviews should be conducted with care, respecting the cultural sensitivities and ensuring confidentiality.
HR policies should outline the process for conducting exit interviews, including who will conduct them, how the information will be used, and how feedback will be communicated to senior management. This process helps organizations learn from departing employees and make necessary improvements to their HR practices.
8 Special Considerations in the Middle East
8.1 Cultural Sensitivity
- Respect for Diversity: The Middle East is a region with a rich cultural tapestry, consisting of diverse nationalities, languages, and religious practices. HR policies must be crafted with cultural sensitivity in mind to ensure that all employees feel respected and valued. For instance, in the UAE and Saudi Arabia, it is important to accommodate religious practices such as prayer times and fasting during Ramadan. HR policies should also address the observance of religious holidays and ensure that workplace practices do not unintentionally offend cultural norms. Being culturally aware and respectful helps create a harmonious work environment and enhances employee satisfaction.
- Language Policies: In a region where multiple languages are spoken, clear communication is essential. HR policies should consider the language diversity within the organization. For example, while Arabic is the official language in many Middle Eastern countries, English is commonly used in business settings. Policies should ensure that important documents, including contracts and company guidelines, are available in the languages most understood by employees. This approach not only improves communication but also ensures that all employees fully understand their rights and responsibilities.
8.2 Nationalization Policies (Emiratization and Saudization)
Many Middle Eastern countries have nationalization programs designed to increase the employment of local citizens in the workforce. Emiratization in the UAE and Saudization in Saudi Arabia are prime examples. These policies require organizations to meet specific quotas for employing local nationals.
HR policies should include strategies for compliance with these programs, such as prioritizing the recruitment of nationals for certain positions and offering training programs to develop local talent. Meeting these nationalization targets is not just a legal requirement but also a contribution to the socio-economic development of the region.
Conclusion
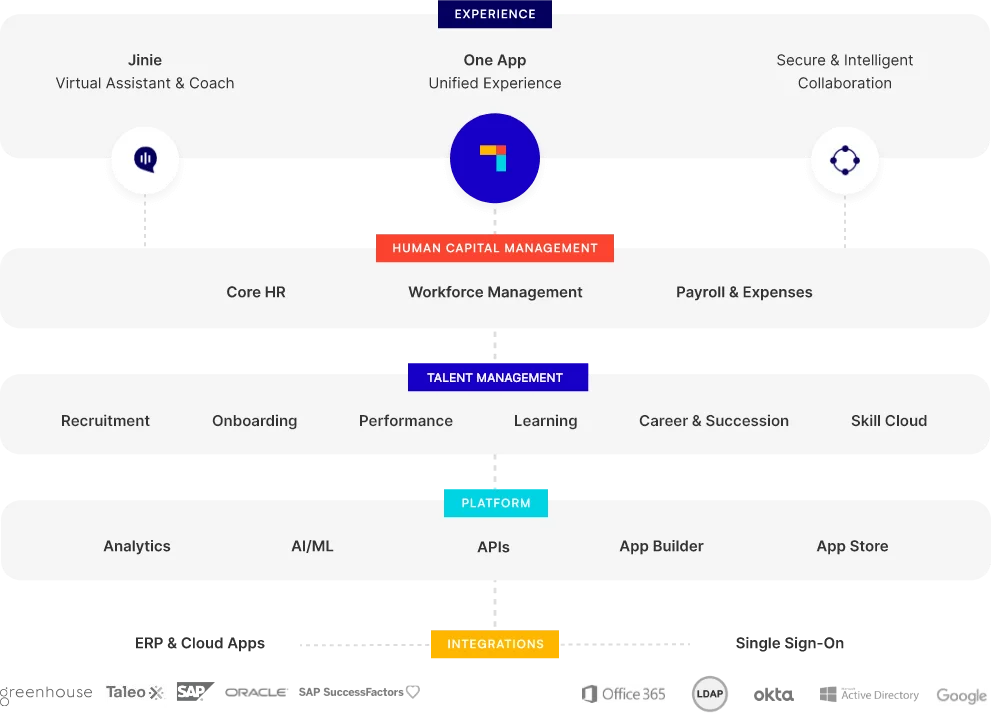
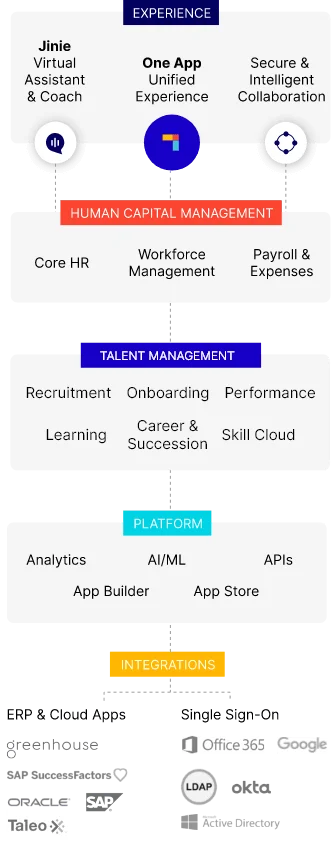
Comprehensive HR policies are key to successful employee management and growth in the Middle East. These policies not only ensure legal compliance but also create a workplace where employees feel valued and motivated. With modern workforce dynamics, HCM software like PeopleStrong has become essential for managing and applying HR policies efficiently.
PeopleStrong provides a centralized platform where organizations can consistently implement HR policies, track compliance, and easily update them when necessary. Its user-friendly interface simplifies tasks like payroll, performance evaluations, and talent management, freeing up HR teams to focus on strategic initiatives that enhance employee engagement.
One standout feature is PeopleStrong’s employee self-service portal, where staff can access HR policies, ensuring clarity and compliance across the organization. This empowers employees by providing them with clear expectations and easy access to important guidelines.
By leveraging PeopleStrong, Middle Eastern businesses can automate their HR processes, streamline operations, and ensure that their policies are accessible and effectively applied. This not only meets the evolving needs of today’s workforce but also positions organizations for long-term success in the region.
Ready to elevate your HR management? Discover how PeopleStrong can transform your HR processes and drive success for your organization in the Middle East.