The Middle East presents a unique and dynamic environment for businesses, characterized by rapid economic growth, diverse cultural influences, and complex political landscapes.
Developing a robust HR strategy in this region is crucial for organizational success.
The Middle East is experiencing significant changes driven by technological advancements, economic diversification, and evolving workforce expectations.
According to a Deloitte report, 69% of Middle Eastern organizations use data analytics for HR decision-making. This highlights the growing importance of data-driven approaches in managing human resources.
Additionally, Microsoft’s Work Trend Index reveals that 50 percent of MENA (Middle East and North Africa) employees report high stress levels, underscoring the need for effective HR strategies that prioritize employee well-being.
In terms of gender diversity, the region is making strides. A report by Mercer, a global consulting firm, indicates that around 50% of HR executives in the UAE are women. This statistic reflects the progress being made toward gender equality in the workplace, particularly in leadership roles.
The Middle East’s economic landscape is evolving rapidly. Countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE are leading efforts to diversify their economies beyond oil, investing heavily in technology, tourism, and finance sectors.
These changes create opportunities and challenges for HR professionals, who must navigate the complexities of local labour laws, cultural norms, and the expectations of a diverse workforce.
What is HR Strategy & Why is It Important?
A Human Resource (HR) strategy is a comprehensive plan designed to manage and develop an organization’s workforce in alignment with its overall goals and objectives. It encompasses various aspects of human resource management, including talent acquisition, training and development, performance management, compensation, and employee engagement.
An effective HR strategy ensures that the organization has the right people, with the right skills, in the right roles at the right time.
The importance of an HR strategy cannot be overstated. Here are several reasons why a robust HR strategy is crucial for organizational success:
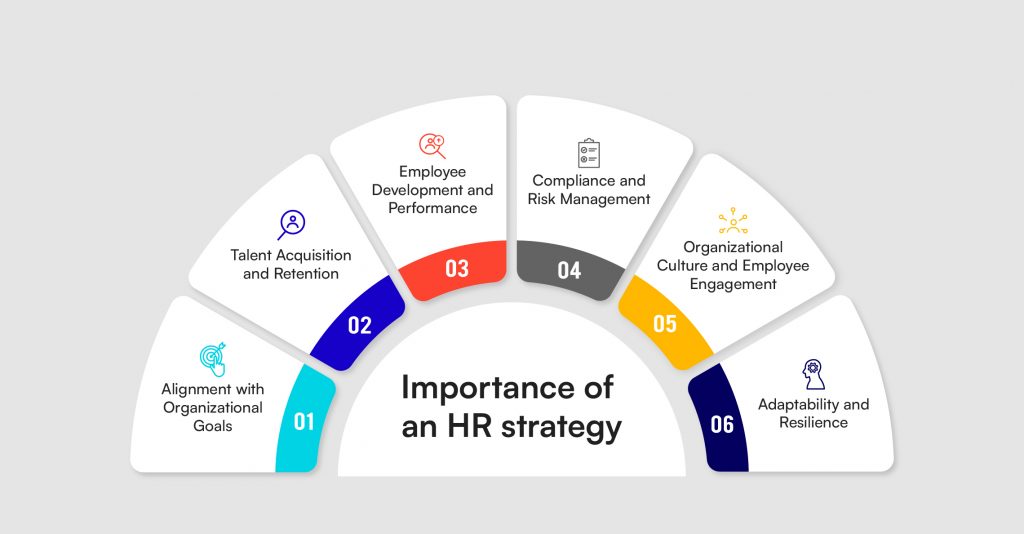
1. Alignment with Organizational Goals
An HR strategy aligns the workforce with the organization’s goals, ensuring that every employee’s efforts contribute to achieving the company’s vision and mission. This alignment fosters a sense of purpose and direction among employees.
According to McKinsey, companies with robust HR strategies are 1.5 times more likely to be prepared for future challenges.
2. Talent Acquisition and Retention
A well-crafted HR strategy helps attract and retain top talent. Effective recruitment, onboarding, and retention practices build a skilled and motivated workforce that drives productivity and growth.
According to LinkedIn, organizations with strong onboarding processes improve new hire retention by 82% and productivity by over 70%.
3. Employee Development and Performance
An HR strategy emphasizes continuous learning and development, ensuring employees acquire new skills and knowledge to stay competitive. It also establishes clear performance metrics and regular feedback mechanisms to enhance employee performance and job satisfaction.
Gallup reports that companies with comprehensive employee development programs see an 11% increase in profitability and a 6% higher employee retention rate
4. Compliance and Risk Management
In regions like the Middle East, where labor laws and regulations can be complex, an HR strategy ensures compliance with local laws, reducing the risk of legal issues and penalties. It also helps manage risks associated with employee relations and workplace safety.
5. Organizational Culture and Employee Engagement
A strong HR strategy promotes a positive organizational culture and fosters employee engagement. It includes initiatives to create a supportive work environment, recognize and reward employee contributions, and address employee concerns.
Gallup found that organizations with high employee engagement see a 21% increase in profitability.
6. Adaptability and Resilience
In a rapidly changing business environment, an HR strategy enables organizations to be adaptable and resilient. It includes plans for workforce planning, succession planning, and crisis management, ensuring the organization can respond effectively to challenges and opportunities.
Understanding Human Resource Management in the Middle East
The Middle East is a region characterized by its rapid economic growth, political stability in certain areas, and a unique cultural landscape. Understanding the specific dynamics of human resource management (HRM) in this region is essential for developing an effective HR strategy.
1. Economic Growth and Political Stability
The Middle East has witnessed significant economic growth over the past few decades, primarily driven by the oil and gas industry. Countries like Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Qatar have leveraged their natural resources to build robust economies. Additionally, efforts to diversify economies away from oil dependency have led to the growth of sectors such as construction, finance, IT, and tourism.
Political stability varies across the region. While countries like the UAE and Qatar enjoy relative stability, others face political uncertainties. This political landscape influences business operations and HR practices. Stable regions attract foreign investments and expatriates, while unstable areas pose challenges in terms of security and workforce management.
2. Influence of Religion and Traditions on Workplace Dynamics
Religion, particularly Islam, plays a significant role in shaping workplace dynamics in the Middle East. Islamic principles and practices influence various aspects of HRM, including working hours, dress codes, and gender interactions. For example, the observance of prayer times, fasting during Ramadan, and religious holidays must be accommodated within workplace policies.
Traditions and cultural norms also impact HR practices. The importance of family and tribal affiliations can influence hiring decisions, promotion practices, and workplace relationships. Respect for hierarchy and seniority is deeply ingrained in many Middle Eastern cultures, affecting communication and decision-making processes within organizations.
3. Importance of Family and Tribal Affiliations in Business
Family and tribal affiliations hold significant importance in the Middle Eastern businesses. These affiliations often dictate business partnerships, hiring preferences, and leadership roles. Understanding and respecting these relationships is crucial for building trust and effective collaboration within organizations.
In many cases, businesses are family-owned and operated, with leadership roles passed down through generations. This can impact succession planning and the implementation of modern HR practices. Organizations need to balance traditional family values with contemporary business strategies to remain competitive.
4. Key Labor Laws and Regulations
Labor laws in the Middle East are diverse and complex, with each country having its own set of regulations governing employment. These laws cover various aspects of employment, including contracts, wages, working hours, leave policies, and termination procedures. Compliance with these regulations is essential to avoid legal issues and ensure fair treatment of employees.
For instance, countries like Saudi Arabia have implemented nationalization programs such as Saudization, which mandate a certain percentage of the workforce to be local nationals.
In Saudi Arabia, 66% of private sector employees are expatriates, navigating labor laws like Saudization.
5. Role of Government Institutions and Policies in HR Practices
Government institutions and policies play a pivotal role in shaping HR practices in the Middle East. Governments in the region have introduced several initiatives to enhance local employment, skill development, and workforce diversity. For example, nationalization programs like Emiratization in the UAE and Nitaqat in Saudi Arabia aim to increase the employment of local nationals in the private sector.
These policies require companies to develop HR strategies that align with government goals while addressing their own business needs. Collaboration with government institutions can provide access to training programs, incentives, and support for compliance with labour laws.
Modules of an Effective HR Strategy
Developing an effective HR strategy involves several key components, each designed to align with organizational goals and address the unique challenges of the Middle East. These components ensure that the organization attracts, develops, and retains the right talent to drive success.
1. Talent Acquisition and Recruitment
- Strategies for Attracting Top Talent: Attracting top talent requires a combination of strong employer branding, competitive compensation packages, and a clear career development path. In the Middle East, leveraging social media, job fairs, and recruitment agencies can enhance visibility and attract diverse candidates.
- Balancing Local Hires and Expatriates: Balancing local hires and expatriates is crucial, especially with nationalization programs in place. Companies should develop targeted recruitment processes to attract qualified local talent while also ensuring that expatriates with essential skills are integrated smoothly into the workforce.
2. Training and Development
- Importance of Continuous Learning and Skill Development: Continuous learning and skill development are vital for maintaining a competitive edge. Organizations should invest in training programs that enhance both technical and soft skills, ensuring employees can adapt to changing market demands.
- Customized Training Programs to Suit Local Needs: Customized training programs that consider local cultural and business practices are essential. This includes language training, cultural sensitivity workshops, and technical courses tailored to the specific needs of the Middle Eastern market.
3. Performance Management
- Setting Clear Performance Metrics: Using a robust performance management system aligned with organizational goals are essential for tracking employee progress and ensuring accountability. These metrics should be transparent, measurable, and regularly reviewed.
- Regular Performance Reviews and Feedback Mechanisms: Regular performance reviews and feedback mechanisms help maintain high-performance levels and employee engagement. Constructive feedback and recognition motivate employees and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
4. Compensation and Benefits
- Competitive Salary Structures: Competitive salary structures are crucial for attracting and retaining talent. Companies should benchmark against industry standards and consider the cost of living in different Middle Eastern countries.
- Benefits that Align with Regional Expectations and Norms: Benefits should align with regional expectations and norms, including healthcare, housing allowances, and education subsidies. Additionally, offering flexible work arrangements and wellness programs can enhance employee satisfaction and retention.
5. Employee Engagement and Retention
- Creating a Positive Work Environment: A positive work environment fosters employee engagement and retention. This includes promoting a healthy work-life balance, ensuring workplace safety, and encouraging open communication.
- Strategies to Retain Top Talent and Reduce Turnover: Retention strategies should focus on career development, recognition programs, and competitive compensation. Engaging employees through regular surveys and feedback sessions helps identify and address potential issues early.
How to Create an HR Strategy
Creating an effective HR strategy involves several well-defined steps. Each step is crucial to ensure that the strategy aligns with the organization’s goals and addresses the unique challenges of the Middle East.
Step 1: Define the HR Vision
Start by defining a clear HR vision that aligns with the overall business strategy. This vision should reflect the organization’s core values and long-term objectives. In the Middle Eastern context, consider incorporating elements that respect local cultural norms and values, such as family orientation and respect for hierarchy. This vision should guide all HR activities and decisions.
Step 2: Conduct a SWOT Analysis
Conduct a SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis to understand the internal and external factors impacting your HR strategy. In the Middle East, strengths might include a diverse talent pool and strong government support for business. Weaknesses could involve strict labor laws and high reliance on expatriates.
Opportunities may arise from economic diversification, while threats could include political instability and fluctuating oil prices. This analysis helps identify critical areas for focus and improvement.
Let’s consider XYZ Corporation, a global tech enterprise, conducting a SWOT analysis for developing its HR strategy.
Strengths: XYZ Corporation has a strong brand reputation, attracting top talent worldwide. It also boasts advanced HR technology and comprehensive employee development programs.
Weaknesses: The company faces high employee turnover rates in certain regions and struggles with aligning global teams with the company’s strategic goals.
Opportunities: Emerging markets offer potential for expansion, and advancements in HR analytics can enhance talent management and performance tracking.
Threats: Intense competition for skilled professionals and rapidly changing labor laws in different countries pose significant challenges. By conducting this SWOT analysis, XYZ Corporation can identify strategic HR initiatives to leverage strengths, address weaknesses, capitalize on opportunities, and mitigate threats.
Step 3: Determine HR Goals
Based on the HR vision and SWOT analysis, set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) HR goals. In the Middle Eastern context, these goals should address local hiring quotas, compliance with nationalization programs (like Saudization and Emiratization), and strategies to improve expatriate-local workforce integration.
Goals might include improving local hiring rates, enhancing employee retention, and developing culturally relevant training programs.
Step 4: Develop HR Strategies
Develop detailed strategies to achieve the HR goals. These should include:
- Talent Acquisition: Strategies to attract both local and expatriate talent, leveraging regional job fairs, partnerships with local universities, and social media.
- Training and Development: Programs tailored to local needs, including language training, cultural sensitivity workshops, and technical skills development.
- Performance Management: Implementing performance metrics that consider regional work ethics and practices.
- Compensation and Benefits: Designing packages that include region-specific benefits such as housing allowances and education subsidies.
- Employee Engagement: Initiatives to foster a positive work environment that respects local customs and encourages open communication.
Step 5: Evaluate and Monitor HR Programs
Implement mechanisms to evaluate and monitor the effectiveness of HR programs. Regular assessments help track progress towards HR goals and identify areas for improvement. Use metrics and KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) that are relevant to the Middle Eastern context, such as compliance with labor laws and employee satisfaction levels.
Step 6: Communicate HR Strategies to Employees
Effective communication is key to the success of an HR strategy. Clearly communicate the HR vision, goals, and strategies to all employees. In the Middle East, this might involve using multiple languages and culturally appropriate communication methods. Ensure that employees understand how these strategies benefit them and contribute to the organization’s success.
Step 7: Continuously Improve HR Strategies
HR strategies should be dynamic and responsive to feedback, performance data, and changing business needs. In the Middle Eastern context, stay updated with regional labor laws, economic changes, and cultural shifts. Foster a culture of continuous improvement within the HR team and encourage innovative solutions to emerging challenges.
Adapting to Regional Specificities
To develop a successful HR strategy in the Middle East, it is essential to adapt practices to regional specificities. Here is how to do that:
1. Navigating Cultural Sensitivities
- Respecting Religious Practices and Holidays: Islam is the predominant religion in the Middle East, and its practices significantly influence workplace dynamics. Organizations should respect prayer times, fasting during Ramadan, and religious holidays. Adjusting work schedules and offering flexibility during these periods can demonstrate cultural sensitivity and enhance employee satisfaction.
- Adapting Workplace Policies to Cultural Norms: Workplace policies should reflect the local cultural norms. This includes understanding gender interactions, dress codes, and communication styles. For example, ensuring that policies accommodate traditional dress codes and segregated workspaces where required can create a more inclusive environment.
2. Embracing Diversity
- Promoting Gender Equality and Inclusion: Gender equality initiatives have led to a 15% rise in female leadership roles across the Middle East. Organizations should implement policies that promote equal opportunities for all employees, regardless of gender. This includes offering leadership development programs for women and creating a supportive environment for diverse cultural backgrounds.
- Supporting Diverse Cultural Backgrounds: The Middle Eastern workforce is a mix of local nationals and expatriates from various countries. Promoting a culture of inclusion where diverse cultural backgrounds are respected and valued can enhance teamwork and innovation. Cultural awareness training has been linked to a 25% increase in team performance.
Offering cultural awareness training and celebrating cultural diversity can foster a sense of belonging.
3. Legal Compliance
- Ensuring Adherence to Local Labor Laws: Compliance with local labor laws is crucial. Each country in the Middle East has specific regulations regarding employment contracts, working hours, minimum wages, and termination procedures. Regularly reviewing and updating HR policies to align with these laws helps avoid legal issues and ensures fair treatment of employees.
- Keeping Up-to-Date with Regulatory Changes: The legal landscape in the Middle East is dynamic, with frequent updates to labour laws and regulations. HR professionals must stay informed about these changes and adapt policies accordingly. This can involve attending industry seminars, consulting with legal experts, and participating in HR networks to share knowledge and best practices.
HDFC ERGO’s HR Strategy Transformation with PeopleStrong
HDFC ERGO, the second-largest private insurance player in India, faced significant challenges as its workforce expanded to over 11,000 professionals across more than 225 branches. This rapid growth necessitated the consolidation of HR practices and the provision of a uniform employee experience (EX) across 600+ locations, especially in tier-four and tier-five towns.
The HR team aimed to leverage technology to revitalize and harmonize the employee experience, crucial for last-mile employees in diverse geographical locations. Their ultimate goal was to implement a Super App for people management that could adapt and scale without frequent process overhauls.
Solution
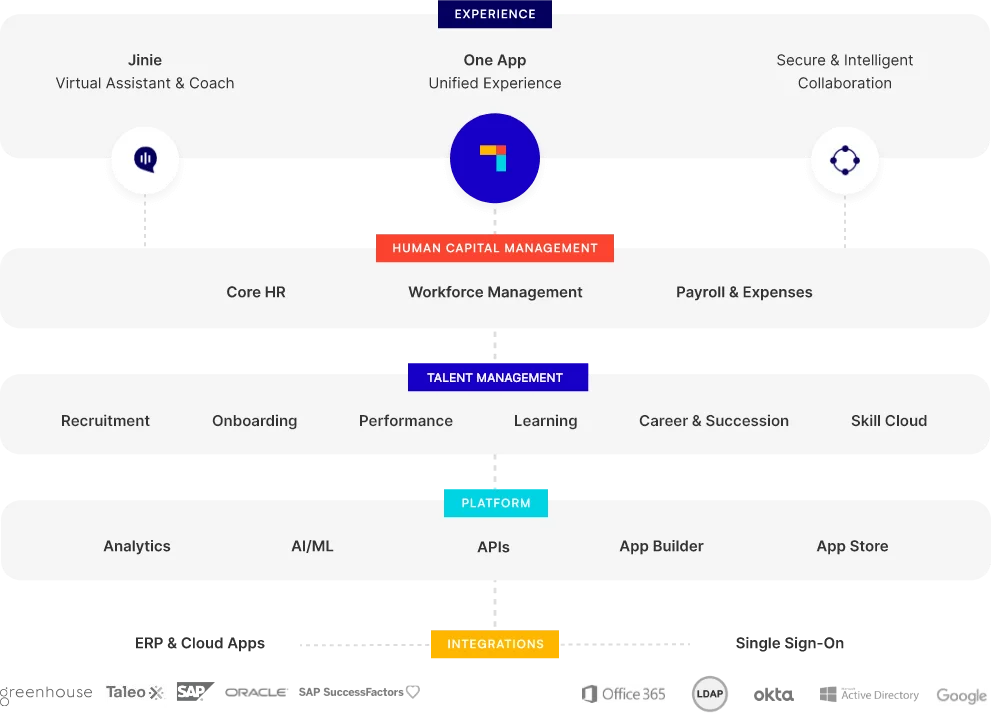
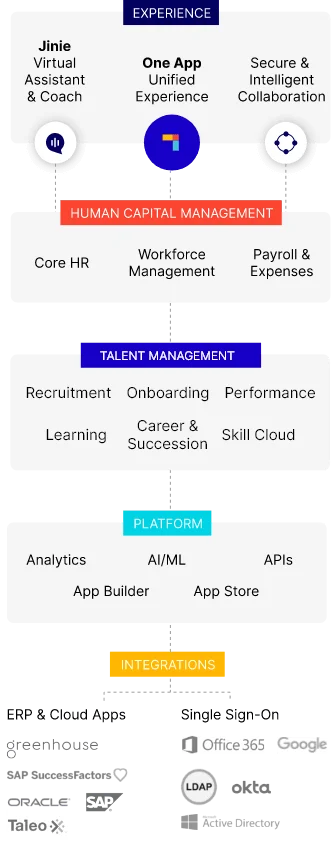
As part of their well-implemented HR strategy, HDFC ERGO partnered with PeopleStrong to develop a comprehensive HR Super App tailored to the needs of its extensive and geographically dispersed workforce. The app included modules for attendance, leaves, approvals, geo-tagging, recruitment, exit management, confirmation, HRIS, transfers, compensation, onboarding, promotions, performance, and analytics.
Key features of the solution included:
- Elastic Hosting and Scalable Architecture: Ensured app robustness under varying workloads.
- Enterprise-Grade Security: Provided a secure mobile-first experience supported by over 2200 SFTP integrations and APIs.
- Simplified Operations: Consolidated all HR practices under a single app, eliminating the need for multiple sign-ons.
- Easy Integration: Allowed for the integration of additional features through island apps for a seamless, single touchpoint experience.
Impact
The implementation of the PeopleStrong Super App had a significant positive impact on HDFC ERGO’s operations and employee experience:
- Rapid Implementation: The app was deployed in just 60 days.
- High Adoption Rate: Achieved a 97% adoption rate within the first 15 days of launch.
- Increased Productivity: Streamlined HR processes and improved efficiency.
- Enhanced Employee Experience: Provided a cohesive and user-friendly platform for HR-related activities.
Sudakshina Bhattacharya, President and CHRO of HDFC ERGO, emphasized the transformative impact of the partnership with PeopleStrong, highlighting the scalability and adaptability of the solution to meet the organization’s growing needs.
HDFC ERGO’s collaboration with PeopleStrong exemplifies a well-implemented HR strategy. By consolidating and streamlining HR processes through a powerful Super App, HDFC ERGO successfully enhanced the employee experience for its 11,000+ workforce. This underscores the importance of leveraging technology in HR strategies to ensure consistent and efficient HR management across all locations, thereby supporting the overall organizational growth and success.
Conclusion
Developing a robust HR strategy tailored for the Middle East requires a nuanced approach that aligns with cultural sensitivities, regional dynamics, and organizational goals.
By understanding local labor laws, embracing diversity, and leveraging technology for efficiency, HR leaders can navigate challenges and foster a productive, engaged workforce.
Remember, continuous evaluation and adaptation are key to ensuring your HR strategy remains responsive to evolving business landscapes in the Middle East. Embrace these principles to empower your organization towards sustainable growth and success.