Repeated and excessive absenteeism can have a huge impact on your business. It leads to decreased productivity, delayed deliverables, increased costs, and an overall indisciplined workforce. However, absenteeism can be tackled by understanding its root cause.
For example, over 22% of workers in the MENA region state low job satisfaction and lack of responsibility as the cause of absenteeism, and both can be tackled by improving workplace policies.
You might think absenteeism is specific to the employee and their personality. They must be indisciplined and unmotivated.
However, high absenteeism is usually caused by the environment surrounding the employee: office culture, peer politics, a lack of career vision, etc.
Effectively managing absenteeism can help leaders build a more reliable, productive, and engaged workforce. The key to tackling absenteeism is identifying its root cause, and to do that, you have first to quantify absenteeism. That is achieved by measuring the ‘absenteeism rate’.
In this article, we explore what the absenteeism rate is, how it’s calculated, and how the root cause of absenteeism can be inferred from this rate.
What Is Absenteeism And ‘Absenteeism (Absentee) Rate’?
Absenteeism refers to habitual, unplanned, and unannounced workplace absences. It also includes being late, leaving early, and taking long breaks during work hours.
Unlike planned leaves, absenteeism is disruptive to the workplace; it often results in incomplete work and missed deadlines. Since it is unplanned, employees usually don’t have a backup plan in place to complete their tasks, which hampers scheduled work deliveries.
It is this disruptive nature that makes absenteeism an important hurdle for management, and the way to measure it is through the absenteeism rate.
The absenteeism rate is calculated by dividing the total number of days lost due to absenteeism by the total number of workdays multiplied by 100 to get a percentage.
Calculating The Absenteeism Rate
To calculate the absenteeism rate, you need to know an employee’s availability (and unavailability) at the office. Attendance systems (biometric scanners, ID card systems, etc) ensure this data is tracked consistently and accurately, allowing you to apply the formula and get a measure of an employee’s absenteeism rate.
1. Track Attendance
Implementing technology like biometric scanners and ID card scanners can track employee attendance. Making it mandatory to log in and out (via card swipes or fingerprint scans) when exiting or entering the work bay can also track break times.
This helps you further analyse how disciplined an employee is.
For example, over report by Teamsense stated that companies using attendance tracking software experience almost a 20% reduction in absence rates.
2. Define The Period For Calculation
The absenteeism rate is calculated over some period, and it’s up to you to define what period you want to consider.
If you intend only to consider unplanned or unexcused absences (which is the ideal method), you can define a short or long timeframe. Since absenteeism is habitual, the rate will remain similar through the months.
However, if you intend to include planned absences as well, it’s more apt to consider a longer timeframe, as everyone occasionally takes planned time off for personal reasons. A shorter timeframe might not be accurate (or fair), especially for employees who were on planned leave during that timeframe.
3. Apply The Formula
Here is the formula to calculate the absenteeism rate:
Absenteeism Rate = ((Number of Unexcused Absences) / Total Time Period) x 100
For example, if an employee took 15 days off in 5 months (150 days), the absenteeism rate would be:
(15/150)x100 = 10%
With that covered, let’s delve into the reasons for absenteeism and tips to tackle it.
Reasons for Absenteeism & How to Tackle Them
1. Workplace Culture
Absenteeism is influenced more by the environment than anything else. The workplace culture shaped by management and peers can foster a strong work ethic if it is positive or result in increased absences if it’s negative and toxic.
Approach:
A supportive and healthy workplace culture will not just reduce absenteeism it will also create a more nurturing and collaborative workplace. Here are a couple of ways you can achieve this:
- Encourage open communication by conducting one-on-one meetings
- Recognize, reward, and celebrate achievements
- Respect and value go a long way
- Conduct wellness programs like getaways and retreats
- Offer flexible work arrangements and a clear leave policy
2. Policies, Or A Lack Thereof
Company policies can affect absenteeism especially if they create a rigid and suffocating workplace. Restricted internet usage, zero tolerance for minor mistakes, etc can be harsh policies that lead to a toxic workplace, and higher absenteeism.
Approach:
Implementing company policies that work for both the company and its employees is important for managing absenteeism effectively. Define clear and balanced policies that are communicated transparently and applied fairly to all employees. Better yet, include employees in the policy definition process so they feel a sense of commitment to these protocols.
3. Unclear Vision & Path
A leadership team without a clear vision contributes to absenteeism. When employees lack direction in their work or opportunities for career development, their motivation and engagement can suffer. Without a defined purpose, they may feel less committed and less inclined to attend work consistently.
Approach:
Setting achievable goals, defining the company’s vision, and setting a clear career path for each employee will motivate them to be present and productive. Here’s how you can do it:
- Give constructive feedback by conducting regular performance reviews
- Create opportunities for employee development by conducting training programs and workshops
- Value every employee’s career growth – encourage open dialogue about career aspirations
- Offer mentorship to guide employees in achieving their professional goals
- Define clear and achievable KPIs
- Recognize and promote (designation, responsibilities, and compensation) top performers
4. Disconnected Leadership
There’s a fine line between giving your team freedom and autonomy and being disconnected from them entirely. Regular meetings, reviewing progress, and offering advice are not signs of micromanagement but are actually key elements of effective leadership.
Leaders who distance themselves from the team, assuming they are providing freedom, risk creating a disengaged workforce. Employees begin feeling undervalued and become less accountable for their work. Eventually, this leads to missed work and absenteeism.
Approach:
Establishing a balance between control and autonomy is key to keeping employees engaged and reducing absenteeism. Here are a few steps you can take:
- Discuss and monitor long-term results while allowing the team to run day-to-day tasks.
- Celebrate and reprimand equally and regularly – this will nurture accountability.
- Create an environment where peers work collaboratively. This creates an atmosphere of camaraderie that encourages employees to show up to work daily.
- Be present and available. Always lead by showing the way.
- Maintain two-way dialogue. Your employees must feel comfortable criticizing you (respectfully, of course).
5. Poor Job Fit
People today have the freedom (and desire) to experiment, learn, and explore different roles and skills. Unlike a few decades ago, when people worked a job until they retired, people today change jobs and roles in pursuit of the right career fit and happiness.
When an employee finds that their role doesn’t align with their skills or interests, it can lead to dissatisfaction and increased absenteeism. It might be a role they applied for, but they can still feel misplaced and unhappy, which eventually leads to them skipping work or taking excessive breaks.
Approach:
- Regularly evaluate employees’ skills and interests to ensure their work matches their capabilities and career goals.
- Ask employees about their interests, and their ideal job or role. If they seem to be a better fit elsewhere, allow them to move departments.
- Be open to adjusting roles or responsibilities based on employees’ feedback and evolving career interests.
Conclusion
Effective absenteeism management involves accurately calculating the absenteeism rate and then investigating its root cause. A good workplace culture, clear policies, career growth opportunities, and support for employees can lead to higher engagement and a lower absenteeism rate.
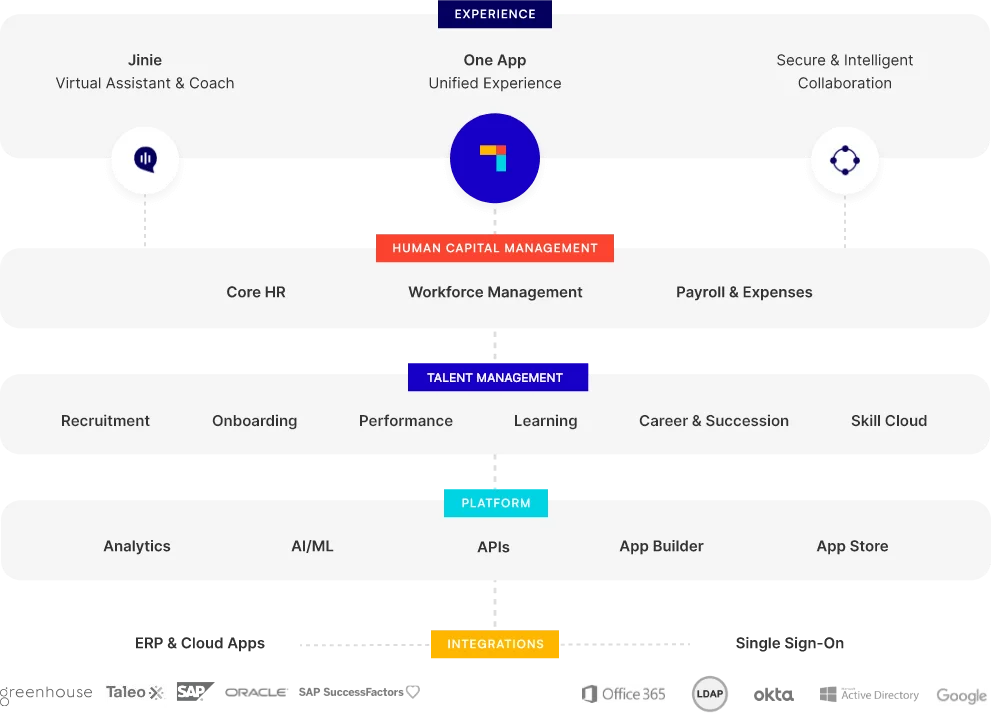
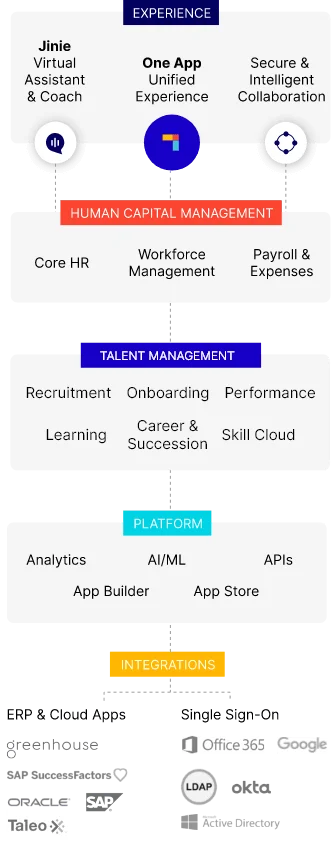
To accurately calculate employee leaves and track absenteeism rates, use absence tracking systems like the one provided by PeopleStrong.
With a thoughtful approach, you can create a more dedicated and productive team.