Remember that awkward moment when your boss asked, ‘Where do you see yourself in five years?’ and you desperately wanted to say, ‘Anywhere but here’?
Performance appraisals have come a long way from such uncomfortable questions. In today’s workplace, they’re not just about ticking boxes or labeling employees as stars or stragglers.
They’re tools for understanding strengths, addressing challenges, and fostering growth. Done right, they can build trust and motivation instead of tension.
But with so many methods out there, finding the most effective ones can feel like navigating a maze.
This guide explores 7 modern methods of performance appraisal that go beyond stereotypes to engage and inspire today’s workforce truly.
- Modern Appraisal Methods Drive Engagement: Approaches like 360-degree feedback, OKRs, and continuous feedback systems focus on collaboration, real-time insights, and aligning individual goals with organizational objectives.
- Customization is Key for Effectiveness: Effective performance appraisals require choosing the right method based on company culture, role-specific needs, and workforce dynamics.
- Technology Enhances Performance Management: Tools like PeopleStrong integrate advanced analytics, real-time feedback, and mobile accessibility, ensuring that performance appraisals are unbiased and adaptable to modern workforce requirements.
What is Performance Appraisal?
A performance appraisal is a formal evaluation process used by organizations to assess an employee’s work performance over a specific period. It involves reviewing an their achievements, strengths, areas for improvement, and contributions to the organization’s goals.
Typically conducted by managers or supervisors, performance appraisals help identify skills, productivity levels, and development opportunities. These reviews often include measurable objectives, qualitative feedback, and sometimes self-assessment from the employee.
The purposes of performance appraisals include:
- Aligning employee goals with organizational objectives.
- Identifying high-performing employees for promotions or rewards.
- Pinpointing areas where additional training or development is needed.
- Providing structured feedback to improve job performance.
- Boosting motivation and engagement by acknowledging achievements.
Modern Vs. Traditional Methods Of Performance Appraisal
Traditional performance appraisals focus on hierarchical evaluations, often emphasizing past performance with limited scope for development. While modern methods adopt a more dynamic, employee-centric approach. Let’s take a look at both of these methods in brief:
1. Traditional Methods Of Performance Appraisal
Here are some methods that organizations have been using traditionally for ages:
- Ranking Method: Employees are ranked from best to worst based on performance.
- Paired Comparison Method: Employees are compared in pairs to identify relative performance.
- Critical Incident Method: Managers record notable positive or negative employee behavior for evaluation.
- Checklist Method: A list of traits or behaviors is used to evaluate performance objectively.
- Graphic Rating Scale: Employees are rated on specific traits or job requirements using a numerical scale.
2. Modern Methods Of Performance Appraisal
Now, let’s look at some popular modern appraisal frameworks that organizations are adapting to:
- 360-Degree Feedback: Comprehensive feedback gathered from peers, subordinates, and supervisors.
- Management by Objectives (MBO): Performance assessed based on the achievement of agreed-upon goals.
- Behaviorally Anchored Rating Scales (BARS): Combines narratives and numerical ratings to evaluate behavior.
- Balanced Scorecard Approach: Measures performance across multiple dimensions, including financial results, customer satisfaction, internal processes, and learning and growth.
- Continuous Feedback Systems: Real-time feedback using technology to support ongoing performance improvement.
- OKR (Objectives and Key Results): A collaborative goal-setting framework that aligns personal objectives with organizational goals and tracks measurable results.
- Peer Reviews: Employees evaluate each other’s work to foster collaboration and accountability, providing insights into teamwork and interpersonal dynamics.
7 Modern Methods Of Performance Appraisal
Modern methods of performance appraisal go beyond annual reviews, offering tools and techniques that focus on continuous growth, employee engagement, and actionable feedback. Let’s take a look at these methods of performance appraisal in detail:
1. 360-Degree Feedback
Imagine getting feedback not just from your boss but also from your teammates, subordinates, and even clients. That’s the beauty of 360-degree feedback—it provides a full-circle view of your performance. Many companies use it to create a culture of transparency and growth.
Why is it so popular? Because it’s not just about what you did; it’s about how you did it. It measures skills like communication, collaboration, and leadership from multiple perspectives. Its unique proposition is its depth and objectivity—by gathering insights from various sources, it eliminates one-sided reviews.
For example, 360-degree feedback can help managers identify hidden talent and leadership potential. It’s especially useful for roles that rely heavily on teamwork and interpersonal skills.
2. Management by Objectives (MBO)
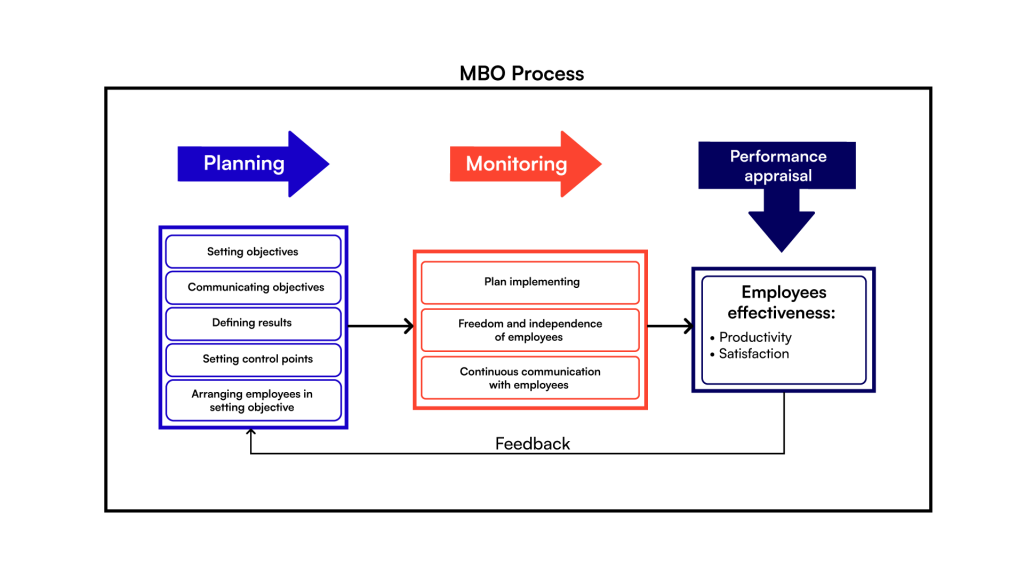
Management by Objectives (MBO) focuses on aligning employee goals with organizational objectives and evaluating performance based on the achievement of these goals.
Unlike traditional methods of performance appraisal that rely on subjective reviews, MBO promotes collaboration between employees and managers to set measurable, clear, and time-bound targets. This approach is widely used by companies where innovation and accountability drive success.
For example, a software developer might aim to reduce application load time by 20% within a quarter. Their appraisal is directly tied to achieving this objective, making the process transparent and results-oriented.
The uniqueness of MBO in appraisals lies in its ability to link individual efforts to organizational success, creating a sense of ownership and motivation. It’s perfect for organizations looking to foster accountability and goal alignment.
3. Behaviorally Anchored Rating Scales (BARS)
Behaviorally Anchored Rating Scales (BARS) is an advanced performance appraisal method that evaluates employees based on specific, predefined behaviors tied to their roles. By focusing on observable actions rather than abstract traits, BARS ensures objective and role-relevant evaluations.
Framework: BARS uses behavior “anchors” to represent various performance levels, each tied to a numerical scale. For example, in customer service:
- Low Performance (1-2): Frequently transfers calls without resolving issues.
- Moderate Performance (3-4): Resolves issues but with limited empathy.
- High Performance (5-6): Resolves issues promptly, proactively suggesting solutions.
It’s ideal for positions where job-specific behaviors define success, such as nurses, sales associates, or customer service representatives. It’s especially effective in reducing biases common in traditional appraisals.
Steps to Implement BARS
- Identify Key Behaviors: Gather examples of effective and ineffective actions using methods like the Critical Incident Technique.
- Group Behaviors: Organize them into performance dimensions relevant to the role, such as communication or problem-solving.
- Assign Ratings: Create a scale, often 1-5 or 1-9, with detailed behavioral anchors for each level.
- Validation: Test the scale with subject matter experts to ensure reliability and consistency.
- Use in Appraisals: Apply the scale during reviews to provide precise, actionable feedback.
4. Balanced Scorecard (BSC)
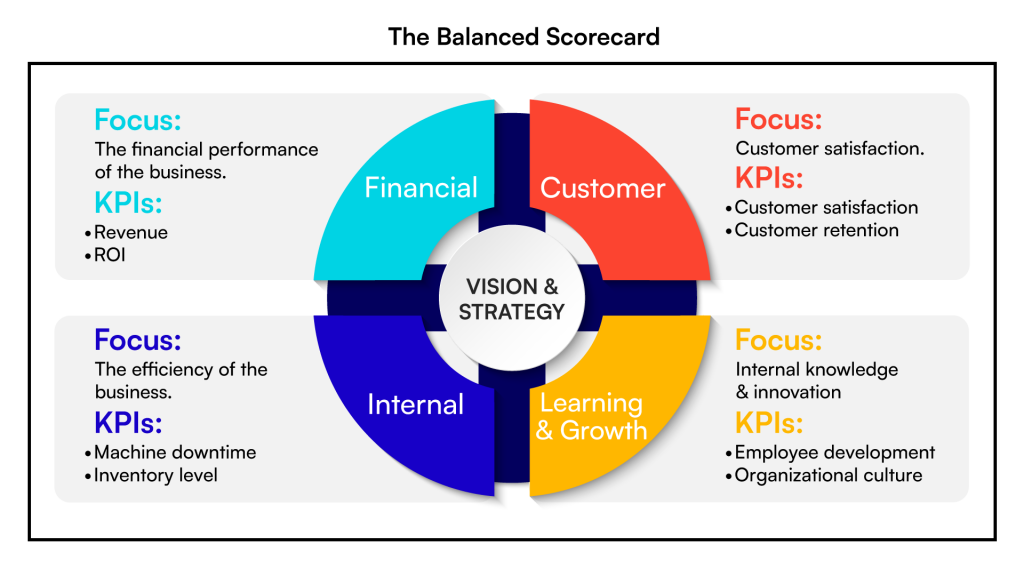
The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is a strategic performance management tool designed to align business activities with an organization’s vision and strategy. Developed by Robert S. Kaplan and David P. Norton, it moves beyond traditional financial metrics to include non-financial measures, offering a more comprehensive view of performance.
Framework: The BSC evaluates organizational performance across four key perspectives:
- Financial: Traditional financial metrics such as revenue growth and return on investment.
- Customer: Measures customer satisfaction, retention, and market share.
- Internal Processes: Evaluate operational efficiency and innovation in processes.
- Learning and Growth: Focuses on employee development, organizational culture, and technological advancements.
How It Works: Goals and metrics are established for each perspective, ensuring all activities align with the organization’s strategic objectives. For example:
- Customer Metric: “Increase customer satisfaction score by 20%.”
- Internal Process Metric: “Reduce production cycle time by 15%.”
The BSC is ideal for organizations aiming to integrate strategy into day-to-day operations. It’s particularly effective for large, complex businesses that require alignment across departments.
Stages of the BSC Method
- Translate Vision: Convert strategic goals into specific objectives for each perspective.
- Set Metrics: Define measurable indicators for objectives, such as KPIs.
- Collect Data: Regularly track performance against metrics.
- Review and Adjust: Use data to identify areas for improvement and refine strategies.
5. Continuous Feedback System
A Continuous feedback system is a dynamic appraisal method where employees receive real-time, ongoing feedback rather than waiting for annual reviews. This approach emphasizes regular communication between managers and employees, promoting a culture of growth and transparency.
The feedback is delivered through informal check-ins, digital tools, or structured weekly or monthly meetings. For instance, a project manager might use a collaborative platform to highlight a team member’s exceptional problem-solving during a client crisis, providing immediate acknowledgment.
Continuous feedback is ideal for fast-paced industries where priorities shift rapidly, such as tech startups or creative agencies. It encourages timely adjustments, improving employee performance and engagement.
6. OKRs (Objectives and Key Results)
OKRs, or Objectives and Key Results, is a goal-setting framework designed to align teams, focus on outcomes, and enhance organizational performance. It integrates ambitious objectives with measurable key results, providing clarity and engagement at all levels of the organization. It:
- Helps prioritize meaningful work.
- Connects individual efforts with organizational goals.
- Enables visibility across teams and departments.
- Empower employees by linking their work to the company mission.
OKRs are ideal for organizations seeking to improve alignment, transparency, and focus. They suit diverse industries and are effective for individual, team, and organizational goal-setting.
Framework
The OKR framework includes three key aspects, including:
- Objective: A clear, inspiring goal that motivates and provides direction (e.g., “Improve customer satisfaction”).
- Key Results: Specific, measurable outcomes tied to the objective (e.g., “Increase Net Promoter Score from 60 to 75”).
- Initiatives: The actions and activities required to achieve the key results (e.g., “Implement a customer feedback tool”).
Implementation Stages
- Define Objectives: Identify inspiring and actionable goals.
- Establish Key Results: Use 3–5 quantifiable metrics for each objective.
- Plan Initiatives: Outline strategic actions to achieve key results.
- Set Timelines: Typically, OKRs are tracked quarterly.
- Review Progress: Use regular check-ins to monitor and adjust.
- Report Results: Share outcomes and learnings with stakeholders.
7. Peer Reviews in Performance Appraisal
Peer reviews involve colleagues evaluating each other’s performance, providing a comprehensive perspective on teamwork, skills, and collaboration. This method complements managerial assessments by focusing on day-to-day interactions and contributions.
Example: In a software development team, peers may evaluate a member’s coding efficiency, contribution to project milestones, and team collaboration. Feedback like, “Consistently meets deadlines but could improve communication during code reviews,” offers actionable insights.
Peer reviews are ideal for roles requiring teamwork or cross-functional collaboration. When structured properly—with clear guidelines and anonymity—they provide valuable insights, help identify development opportunities, and strengthen team dynamics.
Elevate Performance Management with PeopleStrong: The Future of Employee Growth
Choosing the right performance management software isn’t just about streamlining processes—it’s about ensuring the tool aligns with your company’s culture, goals, and growth strategies.
Beyond functionality, consider whether the platform offers integration with existing HR systems, supports real-time feedback, and adapts to the changing dynamics of a modern workforce.
This is where PeopleStrong excels. With its intuitive interface, AI-driven analytics, and comprehensive performance management capabilities, it helps organizations evaluate performance and drive employee engagement, growth, and retention.
Ready to transform your employee performance management?
Let’s talk and explore PeopleStrong’s solutions today.
FAQs
What is the best method for modern performance appraisals?
Methods like 360-degree feedback, OKRs, and continuous feedback systems are popular in modern workplaces due to their focus on collaboration, transparency, and real-time insights.
How does 360-degree feedback improve appraisals?
It gathers input from peers, subordinates, and managers, providing a holistic view of performance. This method enhances fairness and identifies strengths and growth areas.
What is the difference between traditional and modern appraisal methods?
Traditional methods focus on hierarchy and past performance, while modern approaches prioritize collaboration, ongoing feedback, and alignment with organizational goals.
Can performance appraisals improve employee engagement?
Yes, using methods like OKRs and BARS that focus on clarity, measurable goals, and personalized feedback can make employees feel more valued and motivated.
How do organizations choose the right appraisal method?
Organizations should consider workforce needs, company culture, and technological capabilities. Flexible tools like PeopleStrong adapt to diverse appraisal requirements and modern workforce dynamics.