Audit Log Overview
Audit logging is a critical component of any robust Human Resource Management System (HRMS). It involves recording and monitoring activities within the system to maintain data integrity and security. By keeping a detailed log of all user actions, audit logging ensures that every change, access, and modification is tracked. Audit log is non-editable and immutable, ensuring that once an action is logged, it cannot be altered or deleted by any user. This provides a clear log that can be used for various purposes, including security, compliance, and operational transparency.
Benefits of an Audit Log
Audit logs in an HRMS provide numerous benefits that enhance the system’s security, compliance, and operational efficiency. Here are the key advantages:
1. Enhanced Data Security
- Monitoring Access and Changes: Audit logs record who accessed the system, what actions were taken, and when these actions occurred. This helps in monitoring unauthorized access and changes.
- Detecting Suspicious Activities: By keeping a detailed record of all user activities, audit logs can help in detecting and responding to suspicious activities or potential security breaches.
2. Regulatory Compliance
- Adherence to Legal Requirements: Many industries have strict data protection and privacy laws. Audit logs help organizations comply with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and other data protection legislations by providing a transparent record of data handling.
- Audit Trails for Inspections: Audit logs create a historical record that can be reviewed during compliance audits and inspections to demonstrate adherence to required standards.
3. Data Integrity and Accuracy
- Tracking Changes: Audit logs track modifications to employee records, ensuring that data remains accurate and up-to-date. This is crucial for maintaining the integrity of HR data.
- Preventing Data Loss: By documenting all changes, audit logs can help in identifying and restoring accidental data deletions or modifications.
4. Operational Transparency
- Accountability: Audit logs create a culture of accountability by providing a transparent record of who did what and when. This can deter malicious activities and encourage responsible use of the system. HR Manager mostly need this feature for accountability.
- Process Improvement: Analyzing audit logs can provide insights into operational processes, helping to identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies that can be improved.
5. Dispute Resolution
- Evidence in Disputes: In case of disputes or grievances, audit logs serve as a reliable source of truth by providing concrete evidence of actions taken within the HRMS.
- Historical Records: They offer a chronological record of events, which can be crucial in resolving discrepancies or misunderstandings.
6. Performance Monitoring
- User Activity Analysis: Audit logs can be used to analyze user activity patterns, helping to optimize system performance and user experience.
- System Health Checks: Regularly reviewing audit logs helps in maintaining system health by identifying and addressing issues proactively.
7. Support for Investigations
- Internal Investigations: In cases of internal investigations, audit logs provide detailed information that can help in identifying the root cause of issues and determining the appropriate corrective actions.
- External Investigations: Audit logs can also support external investigations by providing transparent and comprehensive records of system activities.
Suggested Read:
13 Best HRMS Software in India: A Comprehensive Guide
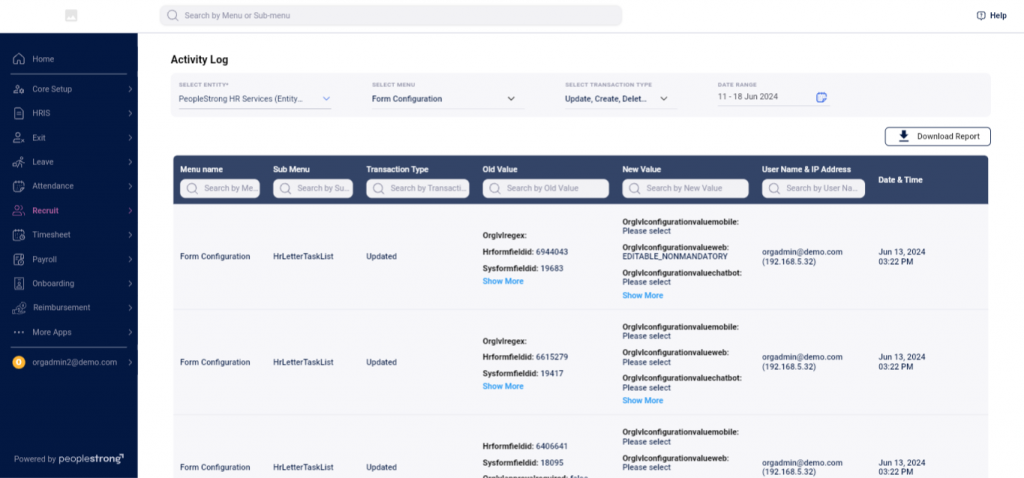
What We Maintain in an Audit Log Report
Audit logs capture detailed information about user activities within the HRMS. This typically includes:
User Detail encompasses the login IDs of users who make configuration changes, including the User ID, User Name, Created By, and Modified By fields. Additionally, the IP Address of the user is recorded, providing essential security information to trace the location or device used for the configuration change.
Organization Detail includes the Organization ID, Organization Name, Entity ID, and Entity Name. These fields help distinguish actions taken within different organizational units and provide a finer level of detail about where within the organization the changes occurred.
Module Detail captures the name of the module where changes were made, such as “Payroll,” “Attendance,” or “Recruitment.” It also records the specific functionality and parameters affected (Topic) and indicates the platform on which the change was made (Operation Type), helping to understand the context and method of the change.
Date and Time Changed Data logs of the date and time of configuration entry (Created Date), the nature of the change (Context), Before Value and After Value fields, which capture the data states before and after the modification. This comprehensive logging ensures every action is traceable and transparent, facilitating security, compliance, and operational efficiency.
This data is stored in a secure, tamper-evident manner to ensure its integrity. The logs can be accessed and reviewed by authorized personnel to monitor system usage and investigate any anomalies.
Audit Log Report Generation
Generating audit log reports involves compiling the recorded data into a comprehensible format. These reports can be customized to focus on specific criteria, such as users, time periods, or actions. Regularly scheduled reports help maintain ongoing oversight, while ad-hoc reports can be generated for specific investigations or audits.
Module Coverage
Audit logging can be implemented across various modules within the HRMS to provide comprehensive oversight:
- Login: Tracking login attempts and user access patterns helps detect unauthorized access and potential security threats, enhancing system security.
- HRIS: Human Resource Information System (HRIS) module encompasses the core components of HR management. Action related to HRIS) asters such as Org Unit, Worksite, Band, Grade, Designation, Group policy, and other configuration changes will be captured in Audit log.
- Recruit: Tracking actions related to candidate data, application statuses, and interview schedules ensures transparency in the recruitment process and compliance with hiring policies.
- Onboarding: Monitoring changes to employee records, benefits, and organizational structures helps maintain data accuracy and accountability in core HR functions.
- Attendance: Recording attendance data modifications and access logs helps ensure accurate tracking of employee attendance and compliance with attendance policies.
- Payroll: Auditing payroll actions, such as salary adjustments and payroll run executions, ensures financial accuracy and compliance with compensation policies.
- Other HR Product Areas: Audit logs can also cover additional HR functions, such as performance management, learning and development, and employee self-service portals, providing a holistic view of system activity.
Challenges in Maintaining Audit Logs
While audit logs offer significant benefits, maintaining them can present several challenges. Here are some key difficulties organizations might face:
1. Storage and Management
- Data Volume: Audit logs can generate a large volume of data, especially in systems with high user activity. Managing and storing this data efficiently can be challenging.
- Retention Policies: Deciding how long to retain audit logs can be difficult, balancing between regulatory requirements and storage limitations.
2. Performance Impact
- System Performance: Continuously logging activities can impact the performance of the HRMS, potentially slowing down other processes.
- Real-Time Processing: Ensuring that audit logs are recorded in real-time without affecting system performance requires efficient logging mechanisms.
3. Security and Privacy
- Protecting Logs: Audit logs themselves can contain sensitive information, making them a target for attacks. Ensuring their security is crucial.
- Access Control: Managing who can view and modify audit logs is essential to prevent unauthorized access and tampering.
4. Compliance and Legal Issues
- Regulatory Requirements: Different regions and industries have varying requirements for audit log retention and management. Keeping up with these regulations can be complex.
- Legal Considerations: Ensuring that audit logs are admissible in legal proceedings requires careful handling and preservation of log integrity.
5. Data Integrity and Consistency
- Log Integrity: Ensuring that audit logs are accurate and unaltered is vital for their reliability. Any discrepancies can undermine their usefulness.
- Consistency Across Systems: In organizations using multiple systems, maintaining consistent logging practices across all platforms can be challenging.
6. Analysis and Utilization
- Data Overload: The sheer volume of audit log data can make it difficult to extract meaningful insights without sophisticated analysis tools.
- False Positives: Identifying real issues among numerous log entries can lead to false positives, making it harder to focus on genuine problems.
7. Technical and Operational Complexity
- Implementation Complexity: Setting up a comprehensive audit logging system can be technically complex and require significant resources.
- Maintenance Effort: Regular maintenance and updates to the logging system are necessary to ensure it continues to function correctly and securely.
8. User Resistance
- Privacy Concerns: Employees might have concerns about being monitored, leading to resistance against the implementation of audit logs.
- Operational Disruption: Introducing new logging procedures can disrupt existing workflows and require user training.
By addressing these challenges with strategic approaches, organizations effectively maintain audit logs while reaping their benefits.
Conclusion
Audit logs are a foundational element of a secure and compliant HRMS. They offer numerous benefits, from ensuring regulatory compliance and protecting data privacy to enhancing accountability and troubleshooting capabilities. By implementing comprehensive audit logging across various HR modules, organizations can maintain the integrity and security of their HR systems, fostering a trusted and efficient workplace environment.