The integration of automation in HR management is transforming modern workplaces. With the rise of digital tools and automation, HR departments are no longer bogged down by repetitive tasks. Instead, they use technology to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and employee satisfaction.
A study by Deloitte shows that 33% of companies have fully automated at least one HR function, and this number is rapidly growing as more organizations recognize the benefits of HR automation.
HR automation transforms how teams manage tasks, shifting focus from manual paperwork to strategic initiatives. Automation covers various HR operations, from recruitment and onboarding to payroll and performance management, enhancing efficiency and reducing errors. This shift enables HR teams to concentrate on higher-value activities that drive business success.
In this blog we will discuss the key aspects of HR automation, exploring its benefits, challenges, practical use cases, and a step-by-step guide to implementing it in your organization.
Let us now explore how HR automation can save time and resources while creating a more efficient and responsive HR department for the future.
What is HR Automation?
HR automation refers to the use of digital tools and software to streamline and automate various human resource processes. It aims to reduce the manual workload on HR professionals by leveraging technology to handle repetitive and administrative tasks. With the help of automation in HR management, the human resource departments can focus on more strategic activities that add value to the organization.
Key components and technologies involved:
- Software and Platforms: HR automation utilizes various software and platforms, such as Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS), Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS), and Learning Management Systems (LMS). These tools integrate seamlessly to provide a comprehensive solution for managing HR processes.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms are employed to enhance decision-making processes in HR. For example, AI can be used in recruitment to screen resumes, schedule interviews, and even predict employee turnover.
- Machine Learning (ML): ML models help in analyzing large sets of HR data to identify patterns and trends. This analysis can inform recruitment strategies, employee development programs, and performance evaluations.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): RPA involves using software robots to mimic human actions and automate routine tasks, such as data entry and report generation.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP enables HR chatbots to interact with employees, answer queries, and assist with tasks like leave applications and benefits inquiries.
Automation in HR management transforms how organizations manage their workforce by making processes more efficient, reducing errors, and providing valuable insights through data analytics.
Benefits of HR Automation
Implementing HR automation can bring a myriad of benefits to an organization. By digitizing and automating routine tasks, HR departments can enhance their efficiency, accuracy, and overall effectiveness. Here are some of the key benefits of integrating automation in HR management:
1. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
HR automation significantly reduces the time spent on administrative tasks, allowing HR professionals to focus on more strategic and value-added activities. Automated systems handle tasks such as data entry, payroll processing, and benefits administration quickly and accurately, leading to increased productivity.
2. Enhanced Accuracy and Reduced Human Error
Manual HR processes are prone to errors, which can lead to costly mistakes and compliance issues. Automation minimizes the risk of human error by ensuring that tasks are performed consistently and accurately. For example, automated payroll systems calculate salaries and deductions precisely, reducing the chances of payroll discrepancies.
3. Improved Employee Experience and Satisfaction
Automation enhances the overall employee experience by providing self-service portals where employees can access and manage their information, such as leave requests, benefits enrollment, and personal details. This empowerment leads to higher employee satisfaction and engagement, as employees can quickly and easily handle their HR-related needs.
4. Cost Savings and Resource Optimization
By automating routine HR tasks, organizations can reduce operational costs associated with manual processing. This includes savings on paper, printing, storage, and labor costs. Additionally, automation allows HR teams to reallocate resources to more strategic initiatives, optimizing the use of human capital within the organization.
5. Data-Driven Decision Making
HR automation systems generate vast amounts of data that can be analyzed to gain valuable insights into various aspects of workforce management. These insights can inform decisions related to recruitment, employee development, performance management, and retention strategies. Data-driven decision-making enables HR departments to implement more effective policies and practices.
6. Compliance and Risk Management
Automated HR systems help ensure compliance with labor laws and regulations by maintaining accurate records and generating timely reports. Automation can also assist in conducting regular audits and ensuring that all HR processes adhere to legal and regulatory requirements, thereby reducing the risk of non-compliance and potential penalties.
Challenges of HR Automation
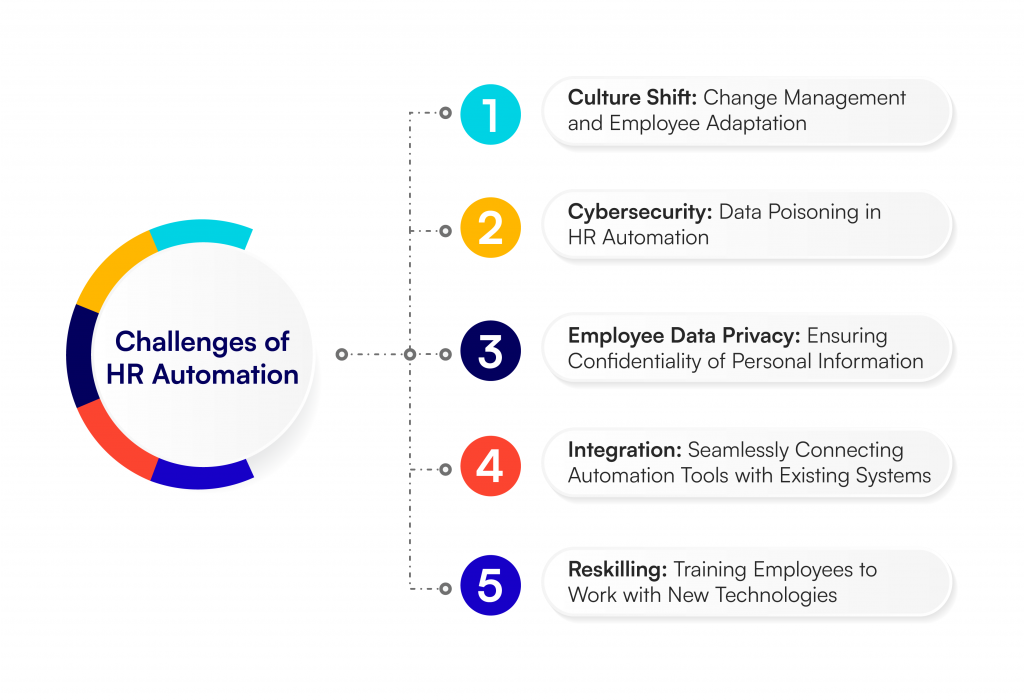
While HR automation offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges that organizations must address to ensure successful implementation and operation. Here are some of the key challenges:
1. Culture Shift: Change Management and Employee Adaptation
Introducing automation into HR processes requires a significant culture shift within the organization. Employees and HR professionals may resist change due to fear of job loss or uncertainty about using new technologies. Effective change management strategies, including communication, training, and support, are essential to help employees adapt to the new automated environment.
2. Cybersecurity: Data Poisoning in HR Automation
HR automation systems that rely on AI and machine learning are particularly vulnerable during the training phase, where data poisoning attacks can occur. Malicious actors can introduce false or harmful data into the training sets, leading to flawed decision-making processes, inaccurate predictions, and potential breaches in the company’s HR systems.
To mitigate this risk, HR leaders should collaborate closely with IT and security teams to establish comprehensive security measures that protect the integrity of HR automation throughout its entire lifecycle.
3. Employee Data Privacy: Ensuring Confidentiality of Personal Information
With the digitization of HR processes, ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of employee data becomes a critical concern. Organizations must comply with data protection regulations and establish strict data privacy policies to safeguard personal information. This includes limiting access to sensitive data and regularly monitoring compliance with privacy standards.
4. Integration: Seamlessly Connecting Automation Tools with Existing Systems
Integrating new HR automation tools with existing systems and processes can be complex and challenging. Organizations need to ensure that their automation solutions can seamlessly connect with other software, such as payroll systems, performance management tools, and employee databases. This integration is crucial for maintaining data consistency and enabling smooth workflows across different HR functions.
5. Reskilling: Training Employees to Work with New Technologies
HR professionals and employees must be trained to effectively use new automation tools and technologies. This reskilling process can be time-consuming and may require additional resources. Organizations should invest in comprehensive training programs to ensure that their HR teams are proficient in using automated systems and can maximize the benefits of automation.
Despite these challenges, the advantages of HR automation far outweigh the difficulties. By addressing these issues proactively, organizations can successfully implement HR automation and reap its numerous benefits.
HR Automation Examples and Use Cases
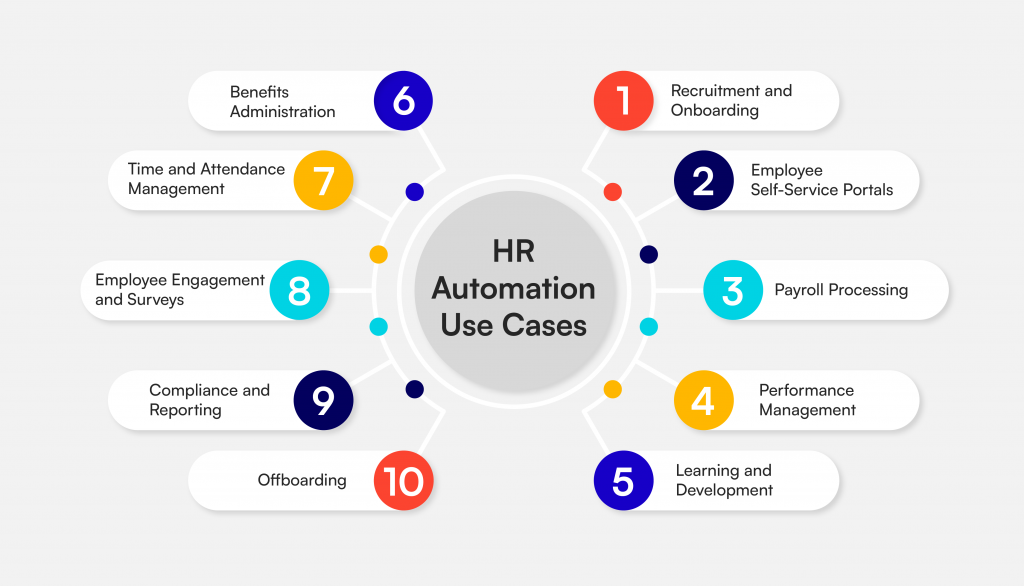
HR automation can revolutionize various aspects of human resources by making processes more efficient and less prone to error. Here are some sophisticated use cases and examples that demonstrate the depth and breadth of HR automation:
1. Recruitment and Onboarding
HR automation can revolutionize the recruitment process by leveraging AI to screen resumes, predict candidate success, and schedule interviews. AI algorithms analyze resume keywords, past job performance data, and social media profiles to rank candidates based on fit.
During onboarding, automation can provision necessary tools, schedule training sessions, and facilitate virtual orientation. For instance, automated systems can send welcome emails, set up payroll accounts, and provide access to company resources, thus reducing time-to-productivity for new hires.
The Osceola County Sheriff’s Office saw an increase in applications from 446 to 1,305 by implementing an automated pre-employment assessment process.
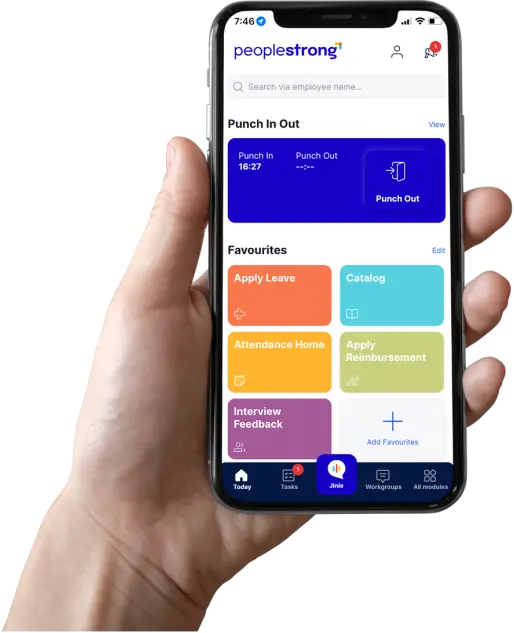
Comprehensive platforms like PeopleStong can integrate with ERP systems to automatically provision access to necessary tools and resources, schedule training sessions, and facilitate virtual orientation. This creates a seamless and engaging onboarding experience, reducing time-to-productivity for new hires.
2. Employee Self-Service Portals
Employee self-service portals empower employees to manage their HR tasks independently. These portals feature AI-driven chatbots that offer 24/7 support for queries related to benefits selection, tax information updates, and employment verification letters. By allowing employees to handle these tasks themselves, HR departments can focus on strategic activities.
For example, an employee can log into the portal to update their address, apply for leave, or check their pay stubs without needing to contact HR directly. This self-service model reduces administrative overhead and enhances the employee experience.
Suggested Read:
Recruitment Process Automation: A Comprehensive Guide
3. Payroll Processing
Automation in payroll processing transforms how businesses manage payroll tasks, replacing manual processes with advanced software solutions. By automating calculations, deductions, and disbursements, companies reduce errors and ensure compliance with complex tax regulations. Integrated with HR and finance systems, automated payroll pulls data directly from attendance records and timesheets, providing up-to-date and accurate calculations.
Automation handles diverse payroll structures, managing everything from basic salaries to bonuses and commissions. It also stays current with legal and regulatory changes, automatically applying the latest tax rates and labor laws, reducing the compliance burden on HR teams.
Solutions like PeopleStrong offer comprehensive payroll automation, handling tasks such as bulk transactions, salary calculations, and the integration of leave and attendance data. These systems consolidate information across HR platforms, facilitating accurate reporting and efficient processing.
Employees benefit from self-service access to payslips, reimbursements, and real-time query management through AI and natural language processing (NLP). The system also manages diverse salary structures and statutory calculations automatically, providing transparency and reliability.
Moreover, PeopleStrong’s advanced analytics and customizable reports support better decision-making for HR and payroll teams.
4. Performance Management
Performance management systems leverage continuous feedback loops and 360-degree reviews to provide comprehensive performance insights. AI-driven analytics identify patterns and predict future performance trends, enabling data-driven decisions for promotions and career development. These systems align individual goals with organizational objectives, ensuring strategic coherence.
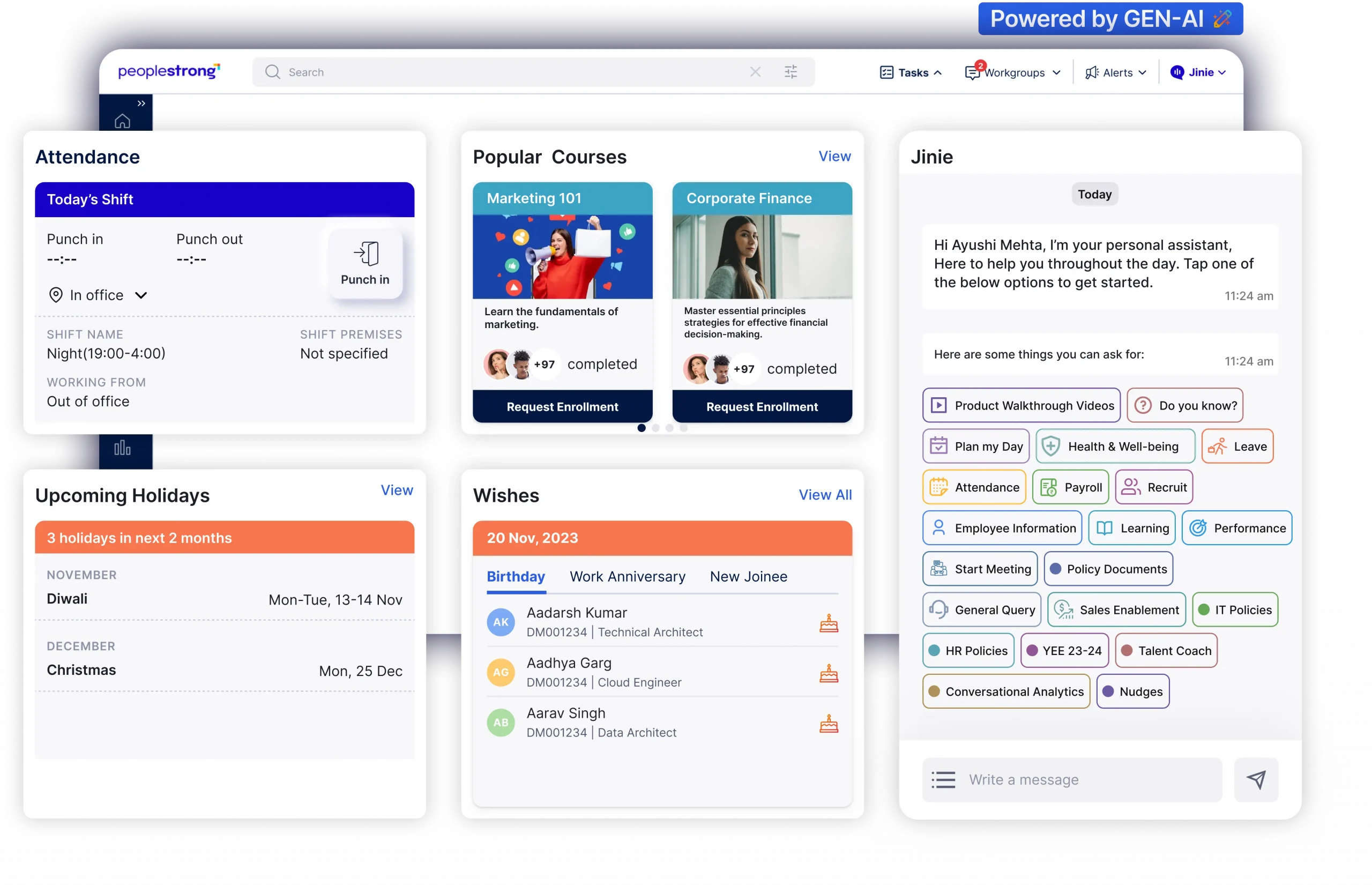
For example, PeopleStrong’s performance management system enhances performance through continuous feedback and 360-degree reviews. The platform aligns individual goals with organizational objectives using frameworks like MBO and OKRs, which can be tracked and shared on any device with automated reminders.
The system supports frequent, meaningful feedback sessions, ensuring upward feedback and one-on-one mentoring. Transparent reviews and powerful performance dashboards eliminate bias and provide real-time tracking to identify and develop high performers. Leveraging performance metrics allows for targeted employee development and skilling plans. PeopleStrong also celebrates achievements, fostering a high-growth culture.
Unlock the potential of your workforce with PeopleStrong’s advanced performance management system. Schedule a demo today!
5. Learning and Development
Automation in learning and development, through platforms like PeopleStrong uses adaptive learning technologies to personalize training programs based on individual employee needs and learning styles.
These platforms track skill development and competency levels, providing actionable insights for workforce planning and development. Integration with career development frameworks ensures that training initiatives are aligned with long-term career progression goals.
PeopleStrong’s learning management system (LMS) offers personalized learning paths aligned with company goals. Employees get AI-powered training recommendations based on their skills and interests, accessible on any device.
Trainers manage courses easily with drag-and-drop tools and automated grading. The system integrates with third-party tools and ensures GDPR and SSO compliance. Real-time dashboards and alerts track progress and boost course completion.
6. Benefits Administration
Automated benefits administration manages complex benefits packages, including flexible spending accounts, wellness programs, and retirement plans. These systems automatically update benefits based on life events, ensuring employees always have access to appropriate benefits.
Predictive analytics help HR teams design more effective and attractive benefits packages by analyzing employee preferences and utilization patterns.
For instance, companies can use healthcare analytics to make informed decisions and ensure compliance with regulations like the Affordable Care
7. Time and Attendance Management
Automated time and attendance systems use advanced technologies such as biometric verification and geofencing to ensure accurate tracking of employee hours. These systems integrate with workforce management software to optimize shift scheduling, reduce labor costs, and ensure compliance with labor laws. Real-time data analytics provide insights into attendance patterns, enabling better resource planning and reducing absenteeism.
For example, platforms like PeopleStrong simplifies time and attendance management for office, home, and remote work environments. Employees can clock in with one tap, and managers have visibility into team availability and absences through geofencing and GPS technology.
The platform supports custom leave types, dynamic approval workflows, and holiday calendars across regions. It ensures compliance with changing laws, integrates with payroll for accurate leave encashments, and includes inbuilt reminders and automatic comp-off calculations for enhanced employee satisfaction.
This not only reduces administrative burden but also provides valuable insights into workforce productivity and helps prevent issues such as employee burnout.
8. Employee Engagement and Surveys
Automated engagement platforms use pulse surveys and sentiment analysis tools to continuously gauge employee morale and engagement levels. These platforms analyze feedback in real-time, providing HR leaders with actionable insights to address issues promptly.
For instance, these automated employee engagement and survey systems can send out regular surveys to measure employee satisfaction, track changes over time, and highlight areas needing improvement. Integration with performance management systems ensures that engagement initiatives are closely aligned with overall employee performance and satisfaction, fostering a positive work culture.
9. Compliance and Reporting
Automated compliance systems continuously monitor changes in labor laws and regulations, ensuring that HR policies and practices remain up-to-date. These systems generate comprehensive compliance reports, conduct regular audits, and maintain secure records of all compliance-related activities.
Their advanced reporting capabilities provide insights into compliance trends and potential risks, enabling proactive management and mitigating legal liabilities.
These tools can track and report compliance with regulations such as the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). This not only mitigates legal risks but also reduces the administrative workload on HR teams, allowing them to focus on strategic initiatives.
10. Offboarding
Comprehensive offboarding automation systems ensure that all necessary steps are completed efficiently and securely when an employee leaves the organization. This includes automated workflows for revoking system access, retrieving company assets, conducting exit interviews, and processing final settlements. Data analytics from these platforms provide insights into turnover trends and inform strategies to improve employee retention.
With the help of these platforms organizations can automate the deactivation of employee accounts, schedule exit interviews, and collect feedback to understand the reasons for departure. This helps protect the company’s assets and data, ensures compliance, and provides insights to improve retention strategies.
How to Automate HR Processes
Implementing HR automation requires a strategic approach to ensure seamless integration and maximize the benefits. Here is a step-by-step guide to HR automation best practices that will help you navigate the process:
Step 1: Identifying Processes for Automation
Start by evaluating your current HR processes to identify which tasks are repetitive, time-consuming, and prone to errors. Common candidates for automation include recruitment, onboarding, payroll processing, benefits administration, time and attendance management, and performance management.
Conduct a thorough analysis to understand the pain points and determine the potential impact of automation on these processes.
Step 2: Selecting the Right HR Automation Tools
Choosing the right tools is critical for successful HR automation. Look for platforms that offer comprehensive solutions and can integrate seamlessly with your existing systems. Consider factors such as scalability, user-friendliness, customization options, and vendor support. Evaluate each tool based on your organization’s specific needs and long-term goals.
Step 3: Integration with Existing Systems
Ensure that the chosen HR automation tools can integrate smoothly with your existing HR systems and other enterprise applications. Integration is crucial for maintaining data consistency and enabling seamless workflows across different functions.
Work closely with your IT team and the software vendors to plan and execute the integration process, addressing any compatibility issues that may arise.
Step 4: Training and Support for HR Staff
Proper training is essential for your HR team to effectively use the new automation tools. Develop a comprehensive training program that covers all aspects of the tools, including basic functionalities, advanced features, and best practices. Provide ongoing support to address any questions or issues that may arise.
Consider appointing a dedicated automation champion within the HR team to oversee the implementation and ensure continuous improvement.
Step 5: Monitoring and Evaluation
After implementing HR automation, it’s important to continuously monitor and evaluate its performance. Use key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of automation on efficiency, accuracy, employee satisfaction, and cost savings.
Collect feedback from HR staff and employees to identify any challenges or areas for improvement. Regularly review and update your automation strategies to ensure they remain aligned with your organization’s goals.
By following these steps, you can successfully implement HR automation in your organization, enhancing efficiency, reducing errors, and freeing up your HR team to focus on strategic initiatives that drive business success.
Conclusion
HR automation is essential for organizations aiming to boost efficiency and productivity. Automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks allows HR teams to focus on strategic initiatives that drive growth.
The advantages of HR automation are numerous: improved accuracy, enhanced employee experience, and cost savings. Despite challenges such as ensuring data security and managing the culture shift, the benefits far outweigh the initial hurdles.
Analyze your current processes, choose the right tools, and ensure they integrate smoothly with your existing systems. Provide comprehensive training and support for your HR team, and continuously monitor the impact of automation to make necessary adjustments.
Embrace HR automation to enhance your department’s capabilities and position your organization for success. Take the first step towards a more efficient, accurate, and employee-centric HR function.
Ready to transform your HR processes with automation? Schedule a demo with us today and see how PeopleStrong can help you streamline operations, enhance employee satisfaction, and drive business success. Don’t wait—start your automation journey now!
FAQs
What are the common challenges HRs face in the recruitment process?
Some of the biggest challenges HRs face are:
- Receiving too many applications and spending hours of time sorting through them to find the best-fit candidates.
- Ensuring that there’s no subjective bias while screening or interviewing candidates for a role.
- Delivering a consistently great candidate experience throughout the recruitment process.
- Verifying that the information provided by candidates in their resumes is correct and that they don’t have a criminal record.
- Reducing the time-to-hire and shortening the recruitment process to include only the most important and necessary steps.
All of these challenges can be overcome by using
What role does technology play in modern recruitment processes?
Recruitment technology has evolved to the point where it will become an inherent part of the hiring process, not just an option but a necessity.
Here are some ways in which technology helps:
- Create detailed job descriptions in seconds, and it automatically suggests the right skills and keywords to add to them based on the role’s requirements.
- Managing various job listings on different channels and providing easy ways to stay on top of things.
- Sorting through hundreds of applications in seconds and using AI to suggest the best-fit candidates.
- Verifying candidates’ educational, employment, criminal, and other records to ensure the details match what they’ve claimed in their resumes.
- Simplifying skill assessments by creating questions and streamlining the scheduling process.
Who is in charge of the recruitment process?
The hiring manager is the one who’s in charge of the recruitment process. This can be a manager of the team for which you’re hiring or a department head.
In some cases, the HR team member who is appointed as the person in charge of hiring for a specific role could also be involved. The respective team’s managers and leaders will still be involved, but the HR person will be the one overseeing everything from start to finish.